The Effect of Exercise on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in Older Adults With and Without Disease: A Meta-Analysis Study
Keywords:
Physical exercise, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), Older adultsAbstract
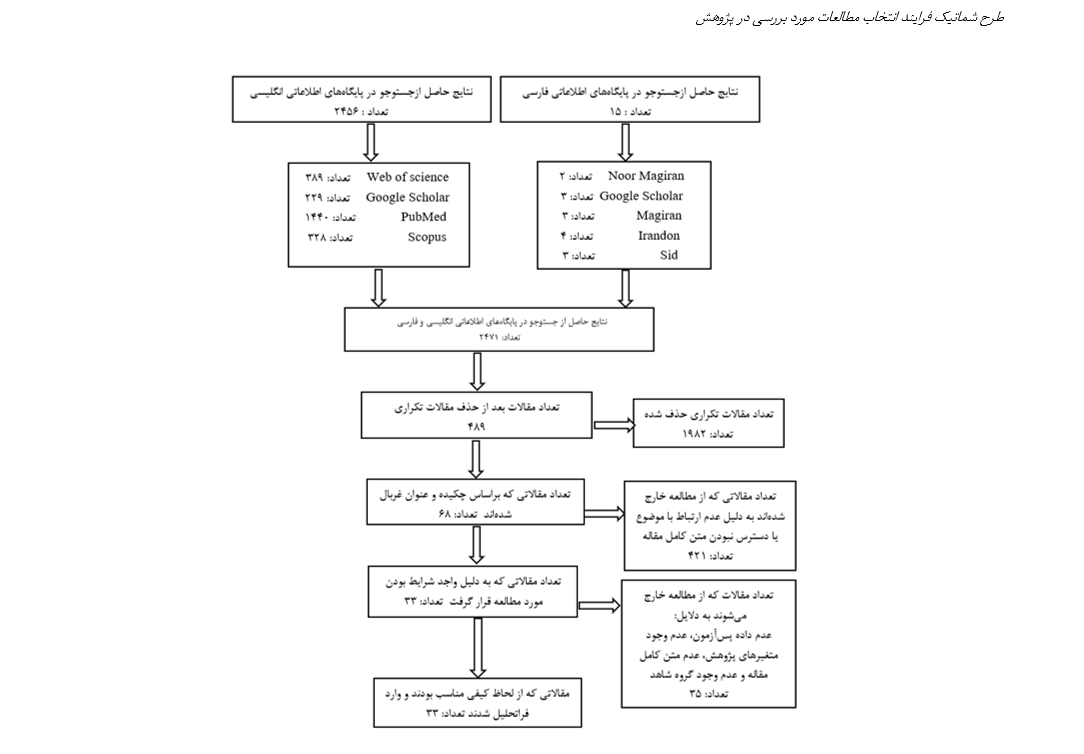
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a crucial protein for neuronal health and function, which declines in older adults, particularly those with medical conditions, potentially leading to cognitive impairments. Physical exercise has been shown to increase BDNF levels. The aim of this study was to systematically collect and analyze existing evidence to evaluate the effects of exercise interventions on BDNF levels in older adults with and without disease. A systematic search was conducted in the databases PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Magiran, Irandoc, NoorMags, and SID to identify articles published from inception until April 2025. To estimate the effect size, the standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals was calculated using CMA2 software. Heterogeneity among studies was assessed using the I² test, and publication bias was evaluated through visual inspection of funnel plots and Egger’s test. Additionally, the quality of the included studies in the meta-analysis was assessed using the PEDro checklist. A total of 33 studies (including 40 exercise interventions) involving 1,099 older adults with and without medical conditions were included in the meta-analysis. The results indicated that exercise interventions led to a significant increase in BDNF levels compared to control groups [SMD= 1.885 (95% CI: 1.326 to 2.444), P < 0.001]. The results of the meta-analysis demonstrated that physical exercise significantly increased BDNF levels in older adults with and without medical conditions, with effects that were statistically significant compared to control groups. These findings highlight that physical activity can serve as an effective strategy to enhance neurological and cognitive health in the elderly.
References
Ali Owsali, S. C., Rahman Soori, Ali Asghar Ravasi, Hossein Mostafavi. (2017). The Effect of three month aerobic exercise whit moderate intensity on BDNF, and cognitive performance in 50-65 years old women with syndrome metabolic. Journal of Sport and Exercise Physiology, 10(1), 47-58. https://doi.org/10.48308/joeppa.2017.98869
Arrieta, H., Rezola-Pardo, C., Kortajarena, M., Hervás, G., Gil, J., Yanguas, J. J., Iturburu, M., Gil, S. M., Irazusta, J., & Rodriguez-Larrad, A. (2020). The impact of physical exercise on cognitive and affective functions and serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in nursing home residents: A randomized controlled trial. Maturitas, 131, 72-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.10.014
Bi, X., Fang, J., Jin, X., & Thirupathi, A. (2024). The interplay between BDNF and PGC-1 alpha in maintaining brain health: role of exercise. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 15, 1433750. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1433750
Byun, J. E., & Kang, E. B. (2016). The effects of senior brain health exercise program on basic physical fitness, cognitive function and BDNF of elderly women - a feasibility study. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem, 20(2), 8-18. https://doi.org/10.20463/jenb.2016.06.20.2.2
Chupel, M. U., Minuzzi, L. G., Furtado, G. E., Santos, M. L., Ferreira, J. P., Filaire, E., & Teixeira, A. M. (2021). Taurine supplementation reduces myeloperoxidase and matrix-metalloproteinase-9 levels and improves the effects of exercise in cognition and physical fitness in older women. Amino acids, 53(3), 333-345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02952-6
Dalirani, M., Gaeini, A. A., & Kordi, M. (2023). Interaction of Vitamin D and Calcium With High-Intensity Circuit Training on BDNF and Fat Percentage of Overweight Elderly. Journal of Sport Biosciences, 15(1), 5-20. https://doi.org/10.22059/jsb.2022.339399.1517
Damirchi, A., Hosseini, F., & Babaei, P. (2018). Mental Training Enhances Cognitive Function and BDNF More Than Either Physical or Combined Training in Elderly Women With MCI: A Small-Scale Study. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen, 33(1), 20-29. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533317517727068
Dana, A., Fallah, Z., Moradi, J., & Ghalavand, A. (2019). The Effect of Cognitive and Aerobic Training on Cognitive and Motor Function, and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factors in Elderly Men. Journal of Sports and Motor Development and Learning, 10(4), 537-552. https://doi.org/10.22059/jmlm.2018.252689.1352
de Azevedo, K. P. M., de Oliveira Segundo, V. H., de Medeiros, G., de Sousa Mata Á, N., García, D., de Carvalho Leitão, J. C. G., Knackfuss, M. I., & Piuvezam, G. (2019). Effects of exercise on the levels of BDNF and executive function in adolescents: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 98(28), e16445. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000016445
Deus, L. A., Corrêa, H. L., Neves, R. V. P., Reis, A. L., Honorato, F. S., Silva, V. L., Souza, M. K., de Araújo, T. B., de Gusmão Alves, L. S., Sousa, C. V., Reis, T. L., de Aguiar, L. S., Simões, H. G., Prestes, J., Melo, G. F., & Rosa, T. S. (2021). Are Resistance Training-Induced BDNF in Hemodialysis Patients Associated with Depressive Symptoms, Quality of Life, Antioxidant Capacity, and Muscle Strength? An Insight for the Muscle-Brain-Renal Axis. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 18(21). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111299
Donyaei, A., Kiani, E., Bahrololoum, H., & Moser, O. (2024). Effect of combined aerobic-resistance training and subsequent detraining on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and depression in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Diabet Med, 41(3), e15188. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.15188
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M., & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. bmj, 315(7109), 629-634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Enette, L., Vogel, T., Merle, S., Valard-Guiguet, A. G., Ozier-Lafontaine, N., Neviere, R., Leuly-Joncart, C., Fanon, J. L., & Lang, P. O. (2020). Effect of 9 weeks continuous vs. interval aerobic training on plasma BDNF levels, aerobic fitness, cognitive capacity and quality of life among seniors with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act, 17, 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11556-019-0234-1
Erickson, K. I., Voss, M. W., Prakash, R. S., Basak, C., Szabo, A., Chaddock, L., Kim, J. S., Heo, S., Alves, H., White, S. M., Wojcicki, T. R., Mailey, E., Vieira, V. J., Martin, S. A., Pence, B. D., Woods, J. A., McAuley, E., & Kramer, A. F. (2011). Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 108(7), 3017-3022. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1015950108
fatemeh dehghan haghighi lotfabadi, A. Y. (2023). The Effect of Aerobic Step Training on Plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Phosphorylated Tau Protein of Elderly Women. New Studies in Sport and Exercise Metabolism, 1(1), 4-0.
Fragala, M. S., Beyer, K. S., Jajtner, A. R., Townsend, J. R., Pruna, G. J., Boone, C. H., Bohner, J. D., Fukuda, D. H., Stout, J. R., & Hoffman, J. R. (2014). Resistance exercise may improve spatial awareness and visual reaction in older adults. J Strength Cond Res, 28(8), 2079-2087. https://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0000000000000520
Frazzitta, G., Maestri, R., Ghilardi, M. F., Riboldazzi, G., Perini, M., Bertotti, G., Boveri, N., Buttini, S., Lombino, F. L., Uccellini, D., Turla, M., Pezzoli, G., & Comi, C. (2014). Intensive rehabilitation increases BDNF serum levels in parkinsonian patients: a randomized study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair, 28(2), 163-168. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968313508474
Fungwe, T. V., Ngwa, J. S., Ntekim, O. E., Allard, J. S., Nadarajah, S., Wolday, S., Ogunlana, O. O., Johnson, S. P., Hughes, K., Larbi, D., Gillum, R. F., & Obisesan, T. O. (2019). Exercise Training Induced Changes In Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Measured Lipid Particles In Mild Cognitively Impaired Elderly African American Volunteers: A Pilot Study. Clin Interv Aging, 14, 2115-2123. https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.S195878
Gholami, F., Mesrabadi, J., Iranpour, M., & Donyaei, A. (2025). Exercise training alters resting brain-derived neurotrophic factor concentration in older adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Exp Gerontol, 199, 112658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2024.112658
Hasanvand, B., & Farhadi, A. (2021). Effect of Combined Exercise and Ginkgo Biloba Supplementation for 8 Weeks on Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Level in Depressed Older Men [Applicable]. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing, 16(2), 234-247. https://doi.org/10.32598/sija.16.2.2805.1
Heissel, A., Pietrek, A., White, S., Kallies, G., Behr, D., Arafat, A., Reischies, F., Heinzel, S., & Budde, H. (2015). Feasibility of an Exercise Program for Older Depressive Inpatients. Geropsych, 28, 163-171. https://doi.org/10.1024/1662-9647/a000134
Hosseinpour Delavar, S., Behpour, N., Tadibi, V., & Ramezankhani, A. (2017). The Effect of 12 Weeks of Cognitive Motor Integrated Exercises on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in the Elderly with Dementia. Journal of Sport Biosciences, 9(2), 223-241. https://doi.org/10.22059/jsb.2017.217453.1114
Hvid, L. G., Nielsen, M. K. F., Simonsen, C., Andersen, M., & Caserotti, P. (2017). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) serum basal levels is not affected by power training in mobility-limited older adults - A randomized controlled trial. Exp Gerontol, 93, 29-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2017.03.019
Jalalian, S., & Ghazalian, F. (2022). The Effect of Twelve Weeks of Physical Exercise with Ginkgo Biloba Supplementation on the Serum Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Inactive Elderly Lifestyle in Tehran [Research]. Razi Journal of Medical Sciences, 29(6), 123-133. http://rjms.iums.ac.ir/article-1-7140-en.html
Kaagman, D. G. M., van Wegen, E. E. H., Cignetti, N., Rothermel, E., Vanbellingen, T., & Hirsch, M. A. (2024). Effects and Mechanisms of Exercise on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels and Clinical Outcomes in People with Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci, 14(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14030194
Kang, D.-w., Bressel, E., & Kim, D.-y. (2020). Effects of aquatic exercise on insulin-like growth factor-1, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and cognitive function in elderly women. Experimental gerontology, 132, 110842. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.110842
Kazemi Nesab, F., & Zafarmand, O. (2024). Comparison of the effects of high-intensity intermittent training and moderate-intensity continuous training on cardiometabolic factors in type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [Review]. Feyz Medical Sciences Journal, 28(1), 96-109. https://doi.org/10.48307/fmsj.2024.28.1.98
Kazeminasab, F., Sharafifard, F., Miraghajani, M., Behzadnejad, N., & Rosenkranz, S. K. (2023). The effects of exercise training on insulin resistance in children and adolescents with overweight or obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 14, 1178376. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1178376
Khalafi, M., Alamdari, K. A., Symonds, M. E., Nobari, H., & Carlos-Vivas, J. (2021). Impact of acute exercise on immediate and following early post-exercise FGF-21 concentration in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis. Hormones (Athens), 20(1), 23-33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-020-00245-3
Khalafi, M., Malandish, A., Rosenkranz, S. K., & Ravasi, A. A. (2021). Effect of resistance training with and without caloric restriction on visceral fat: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev, 22(9), e13275. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13275
khosravi, a., & Taherzadeh, S. (2022). The Effect of a Whole Body Vibration Period on Serum BDNF Levels in Obese Postmenopausal Women. Journal of Applied Health Studies in Sport Physiology, 9(2), 81-92. https://doi.org/10.22049/jahssp.2022.27795.1465
Kim, B. R., & Lim, S. T. (2022). Effects of Leisure-Time Physical Activity on Cognitive Reserve Biomarkers and Leisure Motivation in the Pre-Diabetes Elderly. Healthcare (Basel), 10(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10040737
Kim, H., Lee, D., & Lee, Y. (2022). The Effect of Aerobic Exercise on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Individuals with Mild Cognitive Impairment: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trials. Physical Therapy Rehabilitation Science, 11, 304-310. https://doi.org/10.14474/ptrs.2022.11.3.304
Kim, J. H., & Kim, D. Y. (2018). Aquarobic exercises improve the serum blood irisin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in elderly women. Exp Gerontol, 104, 60-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2018.01.024
Kim, S., Choi, J. Y., Moon, S., Park, D. H., Kwak, H. B., & Kang, J. H. (2019). Roles of myokines in exercise-induced improvement of neuropsychiatric function. Pflügers Arch, 471(3), 491-505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-019-02253-8
Kohanpour, M.-A., Peeri, M., & Azarbayjani, M. A. (2017). The effects of aerobic exercise with lavender essence use on cognitive state and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in elderly with mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Herbmed Pharmacology, 6, 80-84.
Kouhgardzadeh, S., Valipour Dehnou, V., & Molanouri Shamsi, M. (2021). Investigation of the effectiveness of eight weeks of high-intensity functional training in serum levels of factors affecting brain health in elderly men and women [Research]. scientific magazine yafte, 23(4), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.32592/Yafteh.2021.23.4.1
Küster, O. C., Laptinskaya, D., Fissler, P., Schnack, C., Zügel, M., Nold, V., Thurm, F., Pleiner, S., Karabatsiakis, A., von Einem, B., Weydt, P., Liesener, A., Borta, A., Woll, A., Hengerer, B., Kolassa, I. T., & von Arnim, C. A. F. (2017). Novel Blood-Based Biomarkers of Cognition, Stress, and Physical or Cognitive Training in Older Adults at Risk of Dementia: Preliminary Evidence for a Role of BDNF, Irisin, and the Kynurenine Pathway. J Alzheimers Dis, 59(3), 1097-1111. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-170447
Li, X., Han, T., Zou, X., Zhang, H., Feng, W., Wang, H., Shen, Y., Zhang, L., & Fang, G. (2021). Long-term high-intensity interval training increases serum neurotrophic factors in elderly overweight and obese Chinese adults. Eur J Appl Physiol, 121(10), 2773-2785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04746-w
Li, Z., Cui, Z., Wang, T., Zheng, H., Li, K., & Yang, C. (2025). Effect of exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factors in middle-aged and older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Physiology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2025.1599980
Matura, S., Fleckenstein, J., Deichmann, R., Engeroff, T., Füzéki, E., Hattingen, E., Hellweg, R., Lienerth, B., Pilatus, U., Schwarz, S., Tesky, V. A., Vogt, L., Banzer, W., & Pantel, J. (2017). Effects of aerobic exercise on brain metabolism and grey matter volume in older adults: results of the randomised controlled SMART trial. Transl Psychiatry, 7(7), e1172. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2017.135
Mogharnasi, M., Kazeminasab, F., Zafarmand, O., & Hassanpour, N. (2024). The effect of aerobic and resistance training on Omentin-1 and Nesfatin-1 levels in adults: A systematic review and meta -Analysis [Meta-analysis]. Journal of Birjand University of Medical Sciences, 30(4), 295-315. https://doi.org/10.21859/JBirjandUnivMedSci.30.4.295
Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., & Stewart, L. A. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev, 4(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Nay, K., Smiles, W. J., Kaiser, J., McAloon, L. M., Loh, K., Galic, S., Oakhill, J. S., Gundlach, A. L., & Scott, J. W. (2021). Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Beneficial Effects of Exercise on Brain Function and Neurological Disorders. Int J Mol Sci, 22(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084052
Setayesh, S., & Mohammad Rahimi, G. R. (2023). The impact of resistance training on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and depression among older adults aged 60 years or older: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Geriatr Nurs, 54, 23-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.08.022
Taherzadeh, S., Mogharnasi, M., kayedi, A., & rasoulian, b. (2021). The Effect of 6 Weeks of Aerobic Exercise and Aqueous Extract of Caraway Seed on Expression of FNDC5 Gene and Serum Irisin Level in Obese Male Rats. Sport Physiology & Management Investigations, 13(1), 91-103. https://www.sportrc.ir/article_132394_b3b63807dfacd7b81870eab511d2b7ce.pdf
Tarsilla, M. (2008). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Journal of Multidisciplinary Evaluation, 6, 142-148. https://doi.org/10.56645/jmde.v6i14.284
Urzi, F., Marusic, U., Ličen, S., & Buzan, E. (2019). Effects of Elastic Resistance Training on Functional Performance and Myokines in Older Women-A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc, 20(7), 830-834.e832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2019.01.151
Vaughan, S., Wallis, M., Polit, D., Steele, M., Shum, D., & Morris, N. (2014). The effects of multimodal exercise on cognitive and physical functioning and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in older women: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing, 43(5), 623-629. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afu010
Vedovelli, K., Giacobbo, B. L., Corrêa, M. S., Wieck, A., Argimon, I. I. L., & Bromberg, E. (2017). Multimodal physical activity increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and improves cognition in institutionalized older women. Geroscience, 39(4), 407-417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-017-9987-5
Wang, X., Wang, H., Ye, Z., Ding, G., Li, F., Ma, J., & Hua, W. (2020). The neurocognitive and BDNF changes of multicomponent exercise for community-dwelling older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging (Albany NY), 12(6), 4907-4917. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102918
Wen, H., & Wang, L. (2017). Reducing effect of aerobic exercise on blood pressure of essential hypertensive patients: A meta-analysis. Medicine, 96(11).
Zafarmand, O., Mogharnasi, M., & Moghadasi, M. (2024). The effect of exercise training on serum levels of adipokines related to energy homeostasis (adropin, asprosin) and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes or obesity: A Systematic review and meta-Analysis. Journal of Applied Health Studies in Sport Physiology, -. https://doi.org/10.22049/jahssp.2024.29339.1620
Zakavi, I., Valipoor, A., Banihashemi Emam Ghaysi, M., Bijani, B., & Eisazadeh, R. (2015). The Effect of Pilates Exercises on Serum BDNF Level in Elderly Men. Journal of Sport Biosciences, 7(4), 675-688. https://doi.org/10.22059/jsb.2015.57291
Zhang, Q., Zhu, M., Huang, L., Zhu, M., Liu, X., Zhou, P., & Meng, T. (2023). A Study on the Effect of Traditional Chinese Exercise Combined With Rhythm Training on the Intervention of Older Adults With Mild Cognitive Impairment. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen, 38, 15333175231190626. https://doi.org/10.1177/15333175231190626
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 امید ظفرمند (نویسنده); فرناز ترابی

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









