مثلث شناختی در سالمندان ایرانی: با تأكید بر كیفیت خواب و سطح فعالیت بدنی
کلمات کلیدی:
Physical activity, sleep quality, cognitive triad, older adultsچکیده
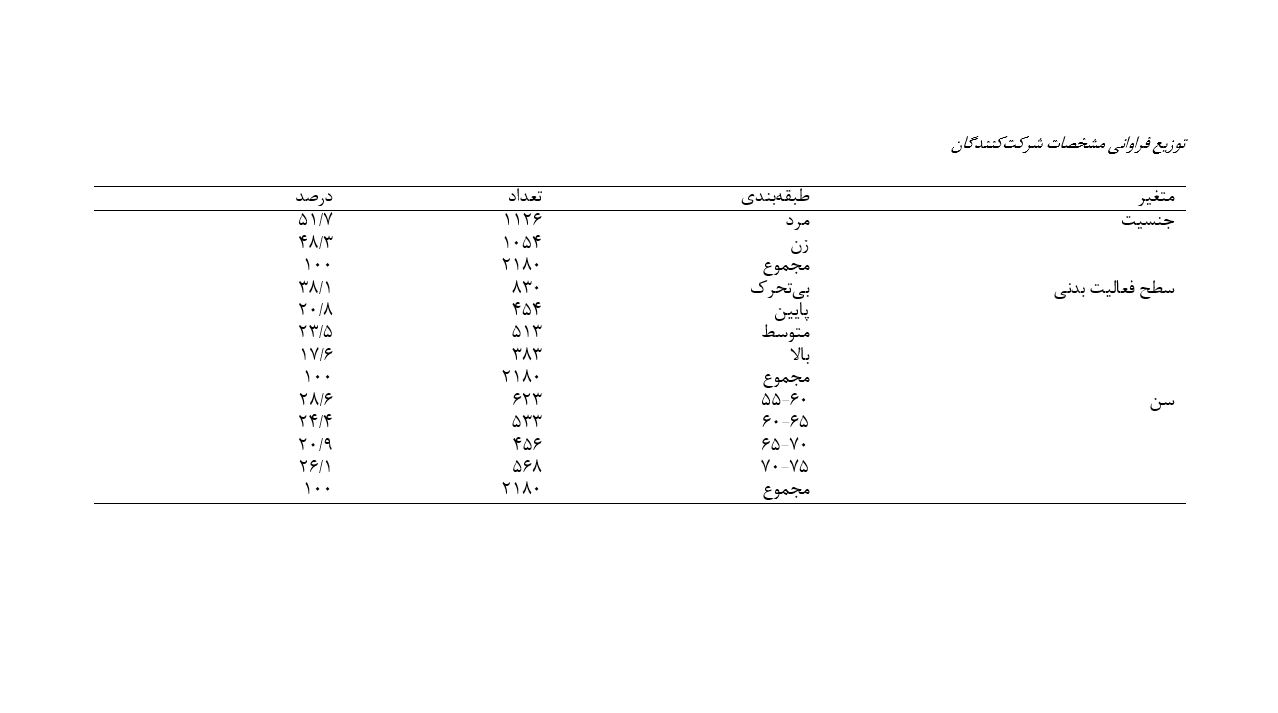
این پژوهش با هدف بررسی نظاممند تأثیر همزمان سطح فعالیت بدنی و کیفیت خواب بر کارکردهای شناختی-هیجانی سالمندان ایرانی پرداخته است. این مطالعه به روش مقطعی-توصیفی و با استفاده از نمونهگیری خوشهای تصادفی چندمرحلهای انجام شد. جامعه آماری شامل 2180 سالمند بالای ۶۰ سال در پنج منطقه جغرافیایی ایران بود. ابزارهای جمعآوری داده شامل پرسشنامه پرسشنامه مثلث شناختی (CTI)، مقیاس کیفیت خواب پیتزبرگ (PSQI) و پرسشنامه سطح فعالیت بدنی سالمندان چامپس بودند. نتایج آزمون تحلیل واریانس چندمتغیرۀ دو راهه(MANOVA) نشان داد که اثرات اصلی سطح فعالیت بدنی و کیفیت خواب و تعامل این دو متغیر برخردهمقیاسهای مثلث شناختی سالمندان معنادار است. نتایج آزمون تعقیبی نشان داد که افزایش سطح فعالیت بدنی، بدون توجه به کیفیت خواب، با بهبود نگرش به خود در سالمندان همراه است (001/0=P)، در مورد نگرش به دنیا، تنها تفاوت معنادار بین گروههای کمتحرک و بیتحرک در افراد با خواب نامطلوب مشاهده شد (05/0=P). مهمتر آنکه در سالمندان با خواب نامطلوب، فعالیت بدنی بیشتر با نگرش مثبتتر به آینده مرتبط بود(05/0≥P)، درحالیکه این رابطه در گروه با خواب مطلوب معنادار نبود. نتایج نشان داد که هم فعالیت بدنی (η2=0.054) و هم کیفیت خواب (η2=0.058) تأثیرات متوسط مستقلی بر خردهمقیاسهای مثلث شناختی دارند، در حالی که اثر تعاملی قویتر (η2=0.1) بوده و سهم قابلتوجهی از واریانس آنها را تبیین میکند. این مطالعه نشان میدهد که فعالیت بدنی میتواند بهعنوان یک عامل تعدیلکننده در رابطه بین کیفیت خواب و نگرشهای شناختی سالمندان عمل کند. بهویژه در افراد با خواب نامطلوب، افزایش فعالیت بدنی با بهبود نگرش به خود و آینده همراه است، که بر اهمیت گنجاندن برنامههای ورزشی در مداخلات سلامت روانی این گروه تأکید دارد. یافتهها از توسعه برنامههای ترکیبی هدفمند که هم به بهبود خواب و هم به افزایش فعالیت بدنی میپردازند، حمایت میکند.
مراجع
1. Asghari, N., Maddahi, M. E., Keraskian Mojmenari, A., & Sahhaf, R. (2020). The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral group therapy (CBT) on psychological symptoms (depression and psychological well-being) in the elderly. Journal of Excellence in Counseling and Psychotherapy, 8(32), 45–58.
2. Chang, S., Cheng, L., & Liu, H. (2024). Effects of three-duration Tai-Chi exercises on depression and sleep quality in older women. European Geriatric Medicine, 15, 1141–1148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-024-00981-4
3. Dong, Y., Zhang, X., Zhao, R., Cao, L., Kuang, X., & Yao, J. (2024). The effects of mind-body exercise on anxiety and depression in older adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15, 1305295. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1305295
4. Gu, S., & Liu, S. (2025). A serial mediation model of physical exercise and loneliness: The role of frailty and depression. BMC Geriatrics, 25, 350. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-025-05988-5
5. Javanmardi, F., Naeimi, E., & Moatamedi, A. (2020). The effectiveness of mindfulness model on improving intimate attitudes and elderly depression. Aging Psychology, 6(1), 39–52. https://doi.org/10.22126/jap.2020.5022.1402
6. Jiang, H., Ding, C., Liu, Y., & Yu, J. (2025). Good sleep quality shields older adults from depressive symptoms linked to isolation: Comparing online and in-person social connections. Geriatric Nursing, 62, 51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2025.01.035
7. Jiang, Y., Zhang, M., & Cui, J. (2024). The relationship between sedentary behavior and depression in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 362, 723–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2024.07.097
8. Karakaya, A., Yıldız, G. N., & Şimşek, N. (2025). Development of the scale on the effects of sleep disorder on stress: Validity and reliability study. BMC Psychiatry, 25, 658. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-025-07099-2
9. Emdadi, P., Pashmdarfard, M., Manouchehri, M., Shokri, K., & Rezaei, M. (2024). Predicting the Resilience of the Elderly in Tehran, Iran, Based on Their Religious Orientation, Mental Toughness, Physical Health, and Sleep Disorders. The Scientific Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 12(6), 1114-1125.
10. Li, B., Jiang, W., Han, S., et al. (2024). Influence of moderate-to-high intensity physical activity on depression levels: A study based on a health survey of Chinese university students. BMC Public Health, 24, 1023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18433-w
11. Li, X., Wang, P., Jiang, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, F., Yan, F., Li, M., Peng, W., & Wang, Y. (2024). Physical activity and health-related quality of life in older adults: Depression as a mediator. BMC Geriatrics, 24, 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04452-6
12. Liu, Y., Tong, Y., Huang, G., et al. (2025). Physical exercise moderates the mediating effect of depressive symptoms between sleep quality and suicidal ideation among college students. Scientific Reports, 15, 21925. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-07767-z
13. Mohammadpanah Ardakan, A., Hemati Farsani, Z., Heydari, Z., & Habibi Ghahfarrokhi, S. (2025). The comparison of the effectiveness of morning and evening exercise on cognitive performance and depression in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Aging Psychology, 11(1), 19–1. https://doi.org/10.22126/jap.2025.10909.1792
14. Saravanan, K., Downey, L., Sawyer, A., Jackson, M. L., Berlowitz, D. J., & Graco, M. (2023). Understanding the relationships between sleep quality and depression and anxiety in neurotrauma: A scoping review. Journal of Neurotrauma, 41(1–2). https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2023.0033
15. Shafaei, H., Najafzadeh, F., Shakki, M., & Ghorbani, S. (2024). Associations between physical activity and quality of life, happiness, and depression among elderly women. Women's Health Bulletin, 11(2), 104–111. https://doi.org/10.30476/whb.2024.101984.1276
16. Sun, M., Zhang, Q., Han, Y., & Liu, J. (2023). Sleep quality and subjective cognitive decline among older adults: The mediating role of anxiety/depression and worries. Journal of Aging Research, 2024(1), 4946303. https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/4946303
17. Taheri, M., Irandost, K., Mirmoezzi, M., & Ramshini, M. (2019). Effect of aerobic exercise and omega-3 supplementation on psychological aspects and sleep quality in prediabetes elderly women. Sleep and Hypnosis, 21, 170–174. https://doi.org/10.5350/Sleep.Hypn.2019.21.0185
18. Wang, J. (2024). The longitudinal relationship between leisure activities and depressive symptoms among older Chinese adults: An autoregressive cross-lagged analysis approach. BMC Public Health, 24, 763. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18293-4
19. Yang, P., Tian, L., Xia, Y., Hu, M., Xiao, X., Leng, Y., & Gong, L. (2025). Association of sleep quality and its change with the risk of depression in middle-aged and elderly people: A 10-year cohort study from England. Journal of Affective Disorders, 373, 245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2024.12.079
20. Yangjian, D., Xinxin, Z., Rongting, Z., Lan, C., Xiaoqin, K., & Jiwei, Y. (2024). The effects of mind-body exercise on anxiety and depression in older adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1305295
21. Zhang, Z., Xu, H., Cui, L., Meng, Y., & Wang, Y. (2025). Sleep disorders accelerate biological aging through depressive symptoms: Evidence from NHANES. Journal of Health Psychology. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1177/13591053251346366
22. Ebrahimpour, Piri, and Jafarnejadgro. (2025). The effect of rehabilitation exercises on the mechanics of transitional movements in healthy individuals: A systematic review. Scientific and Research Monthly of Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, 33(2), 8649-8666.
23. 1. Shafiei Alavijeh. (2017). The relationship between physical activity level, depression and quality of life of the elderly in Alavijeh city, Isfahan. Geriatric Nursing Quarterly, 3(4), 34-45.
24. Beckham, E. E., Leber, W. R., Watkins, J. T., Boyer, J. L., & Cook, J. B. (1986). Cognitive Triad Inventory (CTI)
25. Sahaf, R., Delbari, A., Fadaye Vatan, R., Rassafiani, M., Sabour, M., Ansari, G., et al. (2014). Validity and reliability of self-report physical activity instruments for Iranian older people. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing, 9(3), 206–217.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 فرزانه حاتمي; شفق ابوالقاسمی آتانی (نویسنده)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.









