The Role of Emotional Intelligence and Nutritional Satisfaction in Medication Adherence: A Cross-Sectional Study
Keywords:
Medication adherence, Emotional intelligence, Nutritional satisfaction, Cross-sectional study, TehranAbstract
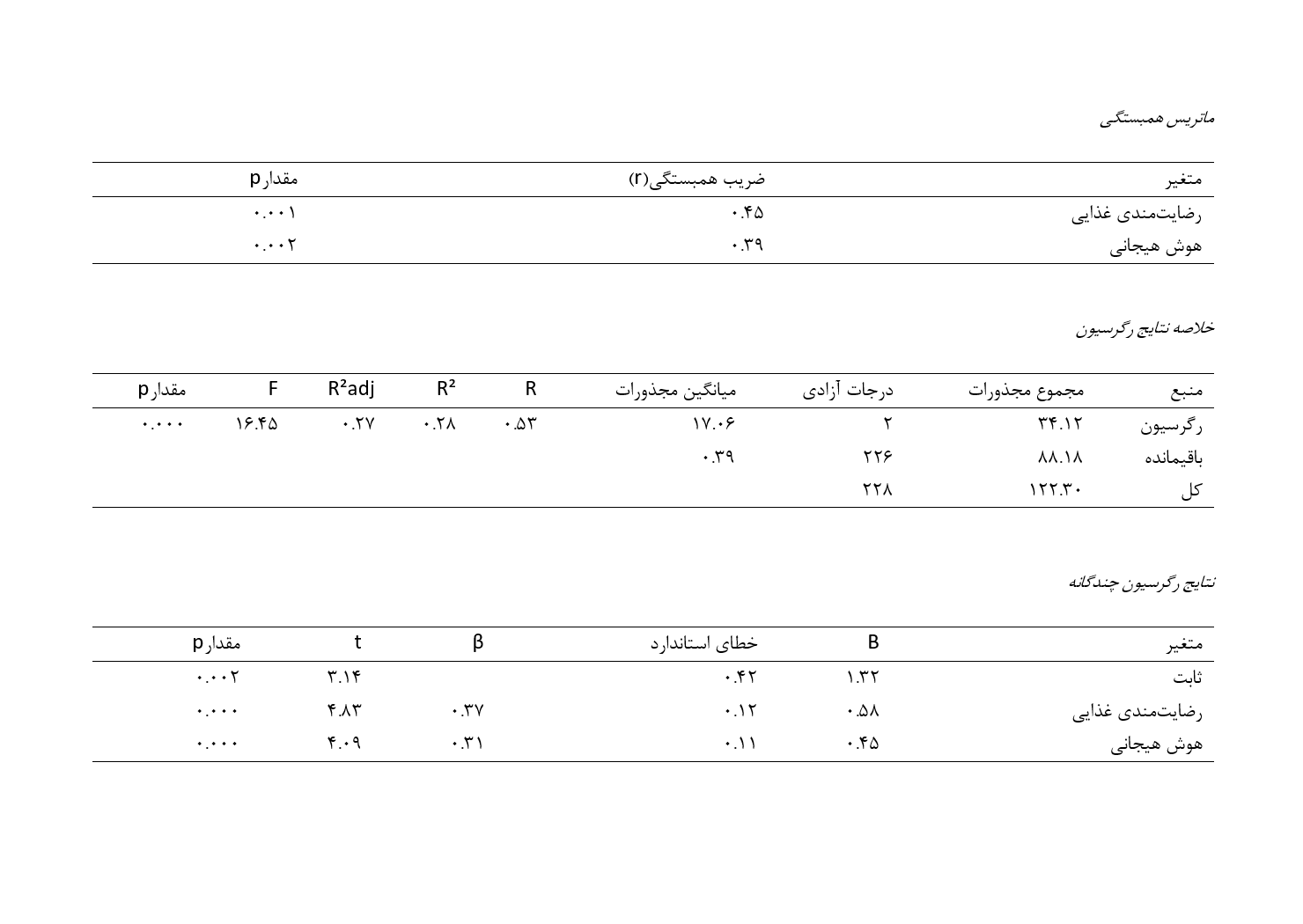
This study aims to investigate the role of emotional intelligence and nutritional satisfaction in predicting medication adherence among residents of Tehran. This cross-sectional study involved 229 participants from Tehran, selected based on the Morgan and Krejcie table. Data were collected using standardized questionnaires for medication adherence, nutritional satisfaction, and emotional intelligence. Pearson correlation and linear regression analyses were performed using SPSS-27 to examine the relationships between variables. The results indicated significant positive correlations between medication adherence and both nutritional satisfaction (r = 0.45, p = 0.001) and emotional intelligence (r = 0.39, p = 0.002). The regression model explained 28% of the variance in medication adherence (R² = 0.28, F(2, 226) = 16.45, p = 0.000). Both nutritional satisfaction (B = 0.58, t = 4.83, p = 0.000) and emotional intelligence (B = 0.45, t = 4.09, p = 0.000) were significant predictors of medication adherence. The study concludes that both emotional intelligence and nutritional satisfaction are significant predictors of medication adherence. These findings suggest that enhancing emotional intelligence and improving nutritional satisfaction may help increase medication adherence, thus improving health outcomes.