Study of the Effect of Organizational Agility on Organizational Health of Employees of Sports and Youth Departments in Alborz Province with the Mediating Role of Central Self-Evaluations
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of organizational agility on organizational health of employees of sports and youth departments of Alborz province with the role of mediator of central self-evaluations. The present study is a descriptive correlational study in which data were collected in the field through a questionnaire and by the field method. The statistical population of the study includes all employees of sports and youth departments of Alborz province, 215 people, of which according to the Krejci and Morgan table (1970), 136 employees of sports and youth departments of Alborz province were selected as a statistical sample by stratified relative random sampling. To collect data, organizational agility questionnaires of Zhang and Sharifi (2000), organizational health of Hui et al. (1996) and self-evaluations of Judge et al. (2003) were used. To analyze the data, correlation coefficient, multiple regression test and structural equation analysis were used. All calculations were performed using PLS and SPSS software. The results showed that organizational agility has an effect on organizational health and central self-evaluations in the sports and youth departments of Alborz province, and 13.76% of the changes in organizational health and 34.57% of the changes in central self-evaluations are explained by organizational agility. Also, central self-evaluations have an effect on organizational health in the sports and youth departments of Alborz province, and 25.40% of the changes in organizational health are explained by central self-evaluations. Also, the results of the Sobel test showed that central self-evaluations have a mediating role in the relationship between organizational transparency and organizational agility on organizational accountability and organizational health. Therefore, it is suggested that providing career growth opportunities, positive feedback, and designing a fair reward system can play an effective role in increasing employees' self-confidence and sense of worth.
The Role of a Healthy Lifestyle and the Interaction of Nutrition and Physical Activity in Slowing Aging and Enhancing Quality of Life: A Systematic Review
Aging is a multidimensional and gradual process shaped by complex interactions among biological, behavioral, and environmental factors. Its consequences affect not only lifespan but also quality of life and functional independence. In recent decades, accumulating evidence has demonstrated that a healthy lifestyle particularly dietary patterns and physical activity plays a decisive role in slowing aging processes and promoting healthy longevity. The aim of this study was to provide a systematic review of molecular-to-clinical evidence on the role of the interaction between nutrition and physical activity as key components of a healthy lifestyle in modulating biological aging pathways and improving quality of life. In this systematic review, studies published in major scientific databases including experimental research, animal studies, clinical trials, and epidemiological investigations were identified, reviewed, and synthesized. The primary focus was on molecular mechanisms associated with aging, including regulation of energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, chronic low-grade inflammation, insulin-related signaling pathways, and epigenetic modifications. In addition, clinical evidence regarding the effects of different dietary patterns (such as caloric restriction, plant-based diets, and Mediterranean dietary patterns) and various forms of physical activity (aerobic, resistance, and combined training) on physical, cognitive, and psychological outcomes in middle-aged and older populations was examined. The findings indicate that healthy nutrition and physical activity act not only as independent determinants of healthy aging but also exert synergistic effects that modulate key cellular aging processes, delay the onset of age-related diseases, and enhance quality of life across physical, psychological, and social domains. This review emphasizes that healthy lifestyle–based approaches, as non-pharmacological interventions, have substantial potential to promote healthy aging and should be considered integral components of public health and clinical strategies in aging societies.
Evaluating the Role of Social Media in Promoting a Health-Oriented Lifestyle and Behavior Change: A Health Management Approach
Social media has become a powerful setting in which health-related information, norms, and everyday lifestyle choices are shaped. Yet its role in promoting a health-oriented lifestyle is not uniform because outcomes depend on content credibility, network dynamics, and contextual constraints such as access costs, infrastructure quality, filtering, and government interference. This study evaluated the role of social media in promoting a health-oriented lifestyle and explained the mechanism of behavior change from a health management perspective using a mixed-methods design. In the qualitative phase, experts in sport, health, and social media were recruited through purposive snowball sampling until theoretical saturation. Interviews were analyzed using systematic grounded theory (open and axial coding) to build a paradigm-based conceptual model. In the quantitative phase, sport media consumers completed a researcher-developed questionnaire; 374 valid responses were analyzed. The measurement and structural models were examined using PLS-SEM (SmartPLS), with convergent validity assessed via AVE and discriminant validity via the Fornell–Larcker criterion. Qualitative findings organized the phenomenon into seven domains: informational factors, cultural factors, campaigns/online communities, communication pathways, intervening factors, contextual conditions, and outcomes, with social media identified as the core phenomenon, behavior change as the main strategy, and a health-oriented lifestyle as the final outcome. Quantitative results showed that all main paths were significant (p < .001): causal conditions predicted the core phenomenon; the core phenomenon predicted strategies; contextual and intervening factors affected strategies; and strategies predicted outcomes. The strongest indicators were sport culture (0.91), communication pathways (0.89), accessible/new information (0.87), and campaigns/online communities (0.81), while intervening constraints were dominated by filtering (0.92) and government interference (0.86). The model explained moderate variance in endogenous constructs (R² = 0.47 for the core phenomenon, 0.45 for strategies, and 0.42 for outcomes). Social media can facilitate healthier lifestyles through staged behavior change, provided that supportive conditions are strengthened and constraining factors are managed.
Dose-response relationship between combined aerobic-resistance training, health-related quality of life, and GDF-15 and MDA levels in adults aged 65 to 85 years
Objective: The aging process is associated with a decline in health-related quality of life (HRQoL), which is often exacerbated by increases in biological markers such as growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) as a marker of cellular vulnerability and stress, and malondialdehyde (MDA) as a marker of lipid oxidative damage. These markers play a key role in predicting physiological decline and age-related diseases. This cross-sectional observational study aimed to investigate the dose-response relationship between combined aerobic-resistance training volume, HRQoL, and serum levels of GDF-15 and MDA in adults aged 65 to 85 years.
Method: 200 participants (105 women, 95 men; mean age 74 ± 2.5 years) were selected from the active elderly community in Tehran. Weekly exercise volume was measured using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ-SF) and divided into three levels (low <150 min/week), moderate (150-300 min), and high (>300 min). HRQoL was assessed with the SF-36 questionnaire, and GDF-15 and MDA levels were determined by fasting blood test. Statistical analysis included multivariate linear regression, ANOVA.
Results: Increasing the training volume was associated with a significant improvement in HRQoL score (β = 0.47, p = 0.001), a decrease in GDF-15 levels (β = 0.35, p = 0.001), and MDA levels (β = 0.30, p = 0.001). The dose-response relationship was nonlinear, and the greatest improvement was observed at moderate to high levels. Gender differences also showed that women showed a better response to moderate training.
Conclusion: Combined aerobic-resistance training can reduce oxidative damage and cellular vulnerability and improve HRQoL. These findings emphasize the need to plan personalized exercise interventions for the elderly.
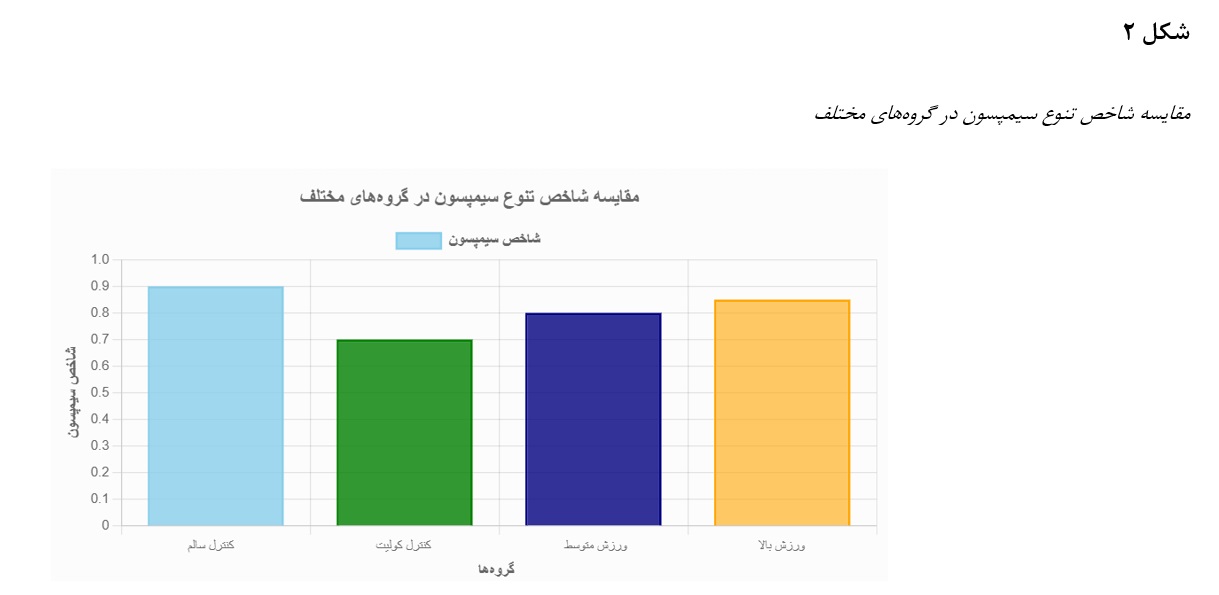
The Effect of High- and Moderate-Intensity Aerobic Interventions on Gut Microbiome Diversity and Function: Investigation of Changes in Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Escherichia coli in Aged Mice
This study aimed to examine the effects of high-intensity (85–100% VO₂max) and moderate-intensity (70–75% VO₂max) aerobic training on microbial diversity (Shannon and Simpson indices) and populations of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and E. coli in aged mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. In this experimental, randomized controlled design, 32 male Wistar mice (18 months old) were divided into four groups (healthy control, colitis control, high-intensity exercise, and moderate-intensity exercise). Colitis was induced using DSS (2–3%) for 7 days. Aerobic training was performed for 8 weeks (five sessions per week) on a treadmill. Microbial diversity was evaluated using 16S rRNA sequencing, quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), and selective culture for Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and E. coli. Data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA and independent t-tests (p ≤ .05). Colitis led to a reduction in Shannon (2.5 ± 0.3) and Simpson (0.7 ± 0.1) indices, a decrease in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, and an increase in E. coli (p < .001). Both high- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise improved microbial diversity (Shannon: 3.2 ± 0.2 and 3.0 ± 0.2, respectively), increased Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, and reduced E. coli (p < .001). High-intensity exercise demonstrated stronger effects (p = .04 for Lactobacillus). Aerobic training, particularly at high intensity, enhances gut microbiome diversity and bacterial balance in aged mice and may serve as a non-pharmacological strategy for managing intestinal inflammation.
Identification of Psychosocial Factors Influencing Older Adults’ Sports Participation: A Systematic Review
Objective: To identify and systematically classify psychosocial factors associated with older adults’ participation in sport, and to examine their interrelationships across individual, social, and structural levels.
Method: A systematic review of international and national peer-reviewed databases using related keywords and their Persian equivalents. Studies meeting inclusion criteria were selected, and data extraction followed a pre-specified form with content analysis grounded in an extracted conceptual framework.
Result: The determinants of older adults’ sports participation clustered into three primary domains: A) Psychological factors: motivation, attitudes, quality of life, and mental health; B) Social factors: social support, interpersonal interactions, policies, technology, the physical environment, and enablers/barriers; C) Barriers: economic, social, and structural. Data synthesis indicates these factors are multidimensional and interrelated.
Conclusion: Participation in sport among older adults is simultaneously shaped by psychosocial and structural factors; neglecting any domain may undermine intervention effectiveness. Findings can inform evidence-based intervention design and policy development to enhance participation rates.
The Effect of Exercise on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in Older Adults With and Without Disease: A Meta-Analysis Study
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a crucial protein for neuronal health and function, which declines in older adults, particularly those with medical conditions, potentially leading to cognitive impairments. Physical exercise has been shown to increase BDNF levels. The aim of this study was to systematically collect and analyze existing evidence to evaluate the effects of exercise interventions on BDNF levels in older adults with and without disease. A systematic search was conducted in the databases PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Magiran, Irandoc, NoorMags, and SID to identify articles published from inception until April 2025. To estimate the effect size, the standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals was calculated using CMA2 software. Heterogeneity among studies was assessed using the I² test, and publication bias was evaluated through visual inspection of funnel plots and Egger’s test. Additionally, the quality of the included studies in the meta-analysis was assessed using the PEDro checklist. A total of 33 studies (including 40 exercise interventions) involving 1,099 older adults with and without medical conditions were included in the meta-analysis. The results indicated that exercise interventions led to a significant increase in BDNF levels compared to control groups [SMD= 1.885 (95% CI: 1.326 to 2.444), P < 0.001]. The results of the meta-analysis demonstrated that physical exercise significantly increased BDNF levels in older adults with and without medical conditions, with effects that were statistically significant compared to control groups. These findings highlight that physical activity can serve as an effective strategy to enhance neurological and cognitive health in the elderly.
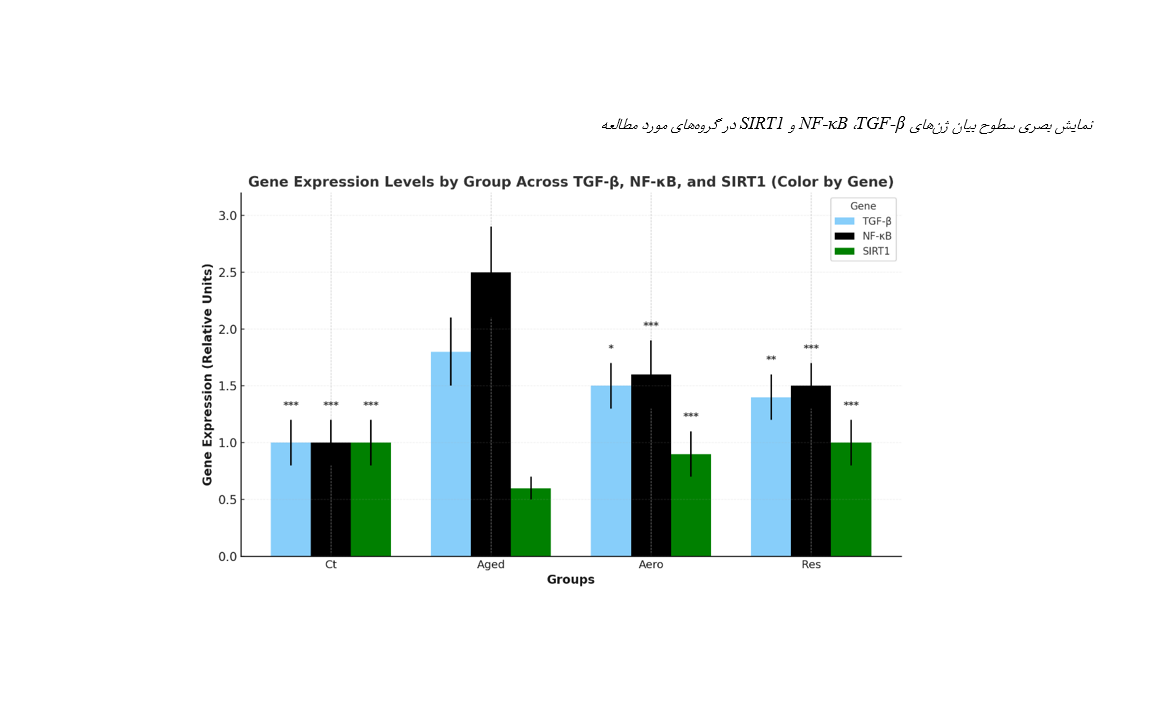
Distinct Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Training on Irisin Levels and the Expression of Inflammatory Genes TGF-β, NF-κB, and SIRT1 in Intestinal Lymphocytes of Aged Rats
This study aimed to investigate the effects of aerobic and resistance training on irisin levels and the expression of the inflammatory genes TGF-β, NF-κB, and SIRT1 in intestinal lymphocytes of aged rats, in order to evaluate noninvasive strategies to mitigate intestinal inflammation during aging. In this laboratory trial, 32 aged male Wistar rats (18 months old) were randomly assigned to four groups: healthy control (Ct), aged without training (Aged), aged with aerobic training (Aero), and aged with resistance training (Res). Training protocols were conducted for 8 weeks (5 days per week); the aerobic group trained at moderate intensity (speed 12 m/min, up to 56 minutes), while the resistance group trained with progressively increasing loads (5% to 40% of body weight, 8 climbs per session). Gene expression was measured using Real-Time PCR, and irisin levels were measured using an ELISA kit. Data were analyzed using SPSS; two-way ANOVA was used to examine the main effects of groups and training types, Tukey's test was used for pairwise comparisons, and independent t-test was used to directly compare the aerobic and resistance groups (p < 0.05). The expression of TGF-β increased in the Aged group compared to Ct (P < 0.001) but showed a significant decrease in both training groups (Aero: 17%; Res: 22%; P < 0.05). NF-κB expression also increased in the Aged group (P < 0.001) and decreased in the training groups (Aero: 36%; Res: 40%; P < 0.001). SIRT1 expression decreased in the Aged group (P < 0.001) and increased in the training groups (Aero: 50%; Res: 67%; P < 0.001). No significant differences were found between Aero and Res for any of the three genes (P > 0.05). Irisin levels increased in both training groups, but the difference between them was not significant (P > 0.05). Aerobic and resistance training can reduce intestinal inflammation and improve intestinal health in aging. Resistance training showed stronger effects, although the differences were not statistically significant. It is recommended that resistance and aerobic training be integrated into exercise programs for the elderly to achieve optimal anti-inflammatory effects.
About the Journal
Longevity aims to advance the scientific understanding and practical application of strategies to extend human lifespan and healthspan. By publishing rigorous, peer-reviewed research, the journal seeks to become a leading platform for disseminating knowledge that bridges basic science, clinical research, public health, and social sciences. Longevity is dedicated to fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation to tackle the complexities of aging and promote healthy living across the lifespan.