تأثیر ۱۲ جلسه تمرینات ثبات پویای عصبی-عضلانی و فالپروف بر تعادل و عملکرد حرکتی زنان سالمند با سابقه سقوط
کلمات کلیدی:
تمرینات ثبات پویای عصبی-عضلانی, فالپروف, تعادل, عملکرد حرکتی, سقوطچکیده
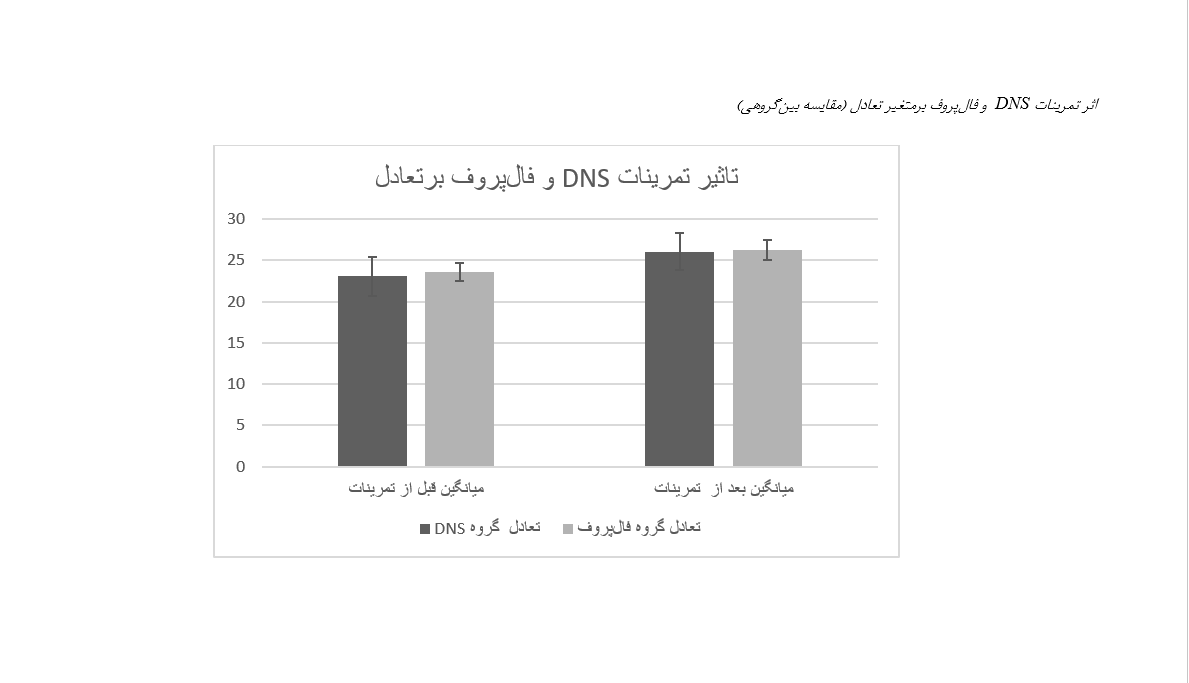
هدف از این پژوهش، مقایسه اثربخشی دو رویکرد تمرینی شامل تمرینات ثبات پویای عصبی–عضلانی (DNS) و برنامه فالپروف بر تعادل و عملکرد حرکتی زنان سالمند با سابقه سقوط بود. در این پژوهش نیمهتجربی، ۳۵ زن سالمند ۶۰ تا ۷۰ ساله با سابقه سقوط بهصورت تصادفی در دو گروه تمرینی DNS (۱۷ نفر) و فالپروف (۱۸ نفر) قرار گرفتند و به مدت چهار هفته، در قالب ۱۲ جلسه تمرین شرکت کردند. برای ارزیابی تعادل از آزمون مینی BEST و برای بررسی عملکرد حرکتی از آزمون ۳۰ ثانیه نشست و برخاست از صندلی (CST) و آزمون ۶ دقیقه راهرفتن (6MWT) استفاده شد. تحلیل دادهها با آزمون تحلیل واریانس با اندازهگیری مکرر و اندازه اثر انجام گرفت. یافتهها نشان داد هر دو برنامه تمرینی باعث بهبود معنادار تعادل و عملکرد حرکتی سالمندان شدند (001/0p<)، اما تفاوت معناداری بین دو گروه مشاهده نشد (05/0p>). اندازه اثر در متغیر تعادل 71/0 و در عملکرد حرکتی 62/0 بود که نشاندهنده اثربخشی بالینی قابلتوجه این تمرینات است. نتایج این تحقیق نشان میدهد تمرینات DNS و فالپروف هر دو میتوانند بهعنوان مداخلهای مؤثر در بهبود تعادل و عملکرد حرکتی زنان سالمند با سابقه سقوط مورد استفاده قرار گیرند. استفاده از این تمرینات در برنامههای پیشگیرانه احتمالاً منجر به کاهش خطر سقوط و بهبود کیفیت زندگی سالمندان میگردد.
مراجع
Alitabar, A., Mohammad Ali Nasab Firouzjah, E., & Shabani, M. (2023). Comparison of the effect of Otago and Fall proof training programs on balance, ankle proprioception and fear of falling in elderly men with a history of falling. Studies in Sport Medicine, 15(36), 123-146. https://doi.org/10.22089/smj.2023.14494.1670
Alvani, Z., & Saheb Al-Zamani, M. (2020). The effect of Dynamic Neuromuscular Stabilization (DNS) exercises on the dynamic balance and functional disability of athletes with non-specific chronic low back pain. Research in Sports Rehabilitation, 8(15), 127-138. https://rsr.basu.ac.ir/article_3870.html
Batistela, R. A., Rinaldi, N. M., & Moraes, R. (2023). Mini-BESTest cutoff points for classifying fallers and non-fallers female older adults. Brazilian Journal of Motor Behavior, 17(4), 126-133. https://doi.org/10.20338/bjmb.v17i4.354
Beyranvand, R., Sahebozamani, M., Daneshjoo, A., & Seyedjafari, E. (2023). Assessment and comparison the effect of exercise in different depth of water on postural stability and balance recovery strategies of older people: a clinical trial. The Scientific Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 11(6), 1002-1015. https://doi.org/10.32598/SJRM.11.6.12
Cheng, D. K., Nelson, M., Brooks, D., & Salbach, N. M. (2020). Validation of stroke-specific protocols for the 10-meter walk test and 6-minute walk test conducted using 15-meter and 30-meter walkways. Topics in stroke rehabilitation, 27(4), 251-261. https://doi.org/10.1080/10749357.2019.1691815
Daneshjoo, A., Sadeghi, H., Yaali, R., & Behm, D. G. (2023). Comparison of unilateral and bilateral strength ratio, strength, and knee proprioception in older male fallers and non-fallers. Experimental Gerontology, 175, 112161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2023.112161
Freund, H.-J. (1983). Motor unit and muscle activity in voluntary motor control. Physiological reviews, 63(2), 387-436. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1983.63.2.387
Gill, S., & McBurney, H. (2008). Reliability of performance‐based measures in people awaiting joint replacement surgery of the hip or knee. Physiotherapy Research International, 13(3), 141-152. https://doi.org/10.1002/pri.411
Khazanin, H., Daneshmandi, H., & Fakoor Rashid, H. (2022). Effect of selected fall-proof exercises on fear of falling and quality of life in the elderly. Iranian Journal of Ageing, 16(4), 564-577. https://doi.org/10.32598/sija.2021.3152.1
Kolar, P., Sulc, J., Kyncl, M., Sanda, J., Neuwirth, J., Bokarius, A. V., Kriz, J., & Kobesova, A. (2010). Stabilizing function of the diaphragm: dynamic MRI and synchronized spirometric assessment. Journal of applied physiology, 109(4), 1064-1071. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01216.2009
Magnani, P. E., Genovez, M. B., Porto, J. M., Zanellato, N. F. G., Alvarenga, I. C., Freire Jr, R. C., & de Abreu, D. C. C. (2020). Use of the BESTest and the Mini-BESTest for fall risk prediction in community-dwelling older adults between 60 and 102 years of age. Journal of geriatric physical therapy, 43(4), 179-184. https://doi.org/10.1519/JPT.0000000000000236
Mahshid, F., Zahra, J., Bayan Peymaneh, S., Ghaem Magham Farahani, Z., & Rahgozar, M. (2008). Normalization of the Brief Cognitive Status Examination of the elderly in Tehran (2006). https://icssjournal.ir/browse.php?a_code=A-10-2-401&slc_lang=other&sid=1
Oliveira, J. S., Gilbert, S., Pinheiro, M. B., Tiedemann, A., Macedo, L. B., Maia, L., Kwok, W., Hassett, L., & Sherrington, C. (2023). Effect of sport on health in people aged 60 years and older: a systematic review with meta-analysis. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 57(4), 230-236. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2022-105820
Orr, R., Raymond, J., & Singh, M. F. (2008). Efficacy of progressive resistance training on balance performance in older adults: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Sports medicine, 38, 317-343. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200838050-00002
Peterka, R. J. (2002). Sensorimotor integration in human postural control. Journal of neurophysiology, 88(3), 1097-1118. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.2002.88.3.1097
Razimoghadam, M., Yaseri, M., Shahali, Z., Fazaeli, A., & Daroudi, R. (2024). The Age and Sex distribution of Hospital Admissions and Hospital Costs with a Focus on the Aging Effect: A Retrospective Analysis of Claims Data. Iranian Journal of Ageing, 18(4), 518-535. https://doi.org/10.21859/sija-1804518
Safari, H., & Zolaktaf, V. (2023). Effects of eight weeks of Dynamic Neuromuscular Stabilization exercises on the balance of older men. The Scientific Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 11(6), 978-987. https://doi.org/10.32598/SJRM.11.6.12
Seidler, R. D., Bernard, J. A., Burutolu, T. B., Fling, B. W., Gordon, M. T., Gwin, J. T., Kwak, Y., & Lipps, D. B. (2010). Motor control and aging: links to age-related brain structural, functional, and biochemical effects. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 34(5), 721-733.
Sherrington, C., Fairhall, N., Wallbank, G., Tiedemann, A., Michaleff, Z. A., Howard, K., Clemson, L., Hopewell, S., & Lamb, S. (2020). Exercise for preventing falls in older people living in the community: an abridged Cochrane systematic review. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 54(15), 885-891. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2019-101516
Sherrington, C., Michaleff, Z. A., Fairhall, N., Paul, S. S., Tiedemann, A., Whitney, J., Cumming, R. G., Herbert, R. D., Close, J. C., & Lord, S. R. (2017). Exercise to prevent falls in older adults: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 51(24), 1750-1758. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096547
Shumway-Cook, A., & Woollacott, M. H. (2007). Motor control: translating research into clinical practice. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.04.004
Stöckel, T., Wunsch, K., & Hughes, C. M. (2017). Age-related decline in anticipatory motor planning and its relation to cognitive and motor skill proficiency. Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 9, 283. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5591340/pdf/fnagi-09-00283.pdf
Takahashi, Y., Saito, K., Matsunaga, T., Iwami, T., Kudo, D., Tate, K., Miyakoshi, N., & Shimada, Y. (2020). Relationship between dynamic trunk balance and the balance evaluation systems test in elderly women. Progress in rehabilitation medicine, 5, 20200004. https://doi.org/10.2490/prm.20200004
Taylor, E. M., Cadwallader, C. J., Curtin, D., Chong, T. T.-J., Hendrikse, J. J., & Coxon, J. P. (2024). High-intensity acute exercise impacts motor learning in healthy older adults. npj Science of Learning, 9(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41539-024-00220-2
Tinetti, M. E., Baker, D. I., McAvay, G., Claus, E. B., Garrett, P., Gottschalk, M., Koch, M. L., Trainor, K., & Horwitz, R. I. (1994). A multifactorial intervention to reduce the risk of falling among elderly people living in the community. New England journal of medicine, 331(13), 821-827. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199409293311301
Yang, Y.-R., Wang, R.-Y., Lin, K.-H., Chu, M.-Y., & Chan, R.-C. (2006). Task-oriented progressive resistance strength training improves muscle strength and functional performance in individuals with stroke. Clinical rehabilitation, 20(10), 860-870. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269215506070701
Zapparoli, L., Mariano, M., & Paulesu, E. (2022). How the motor system copes with aging: a quantitative meta-analysis of the effect of aging on motor function control. Communications Biology, 5(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-03027-2
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 فاطمه منصوربهمنی (نویسنده); سعید بحییرایی; عبدالحمید دانشجو (نویسنده)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.









