Distinct Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Training on Irisin Levels and the Expression of Inflammatory Genes TGF-β, NF-κB, and SIRT1 in Intestinal Lymphocytes of Aged Rats
Keywords:
Inflammation of the intestine, TGF-β, NF-κB, SIRT1, Irisin, aerobic exercise, Resistance trainingAbstract
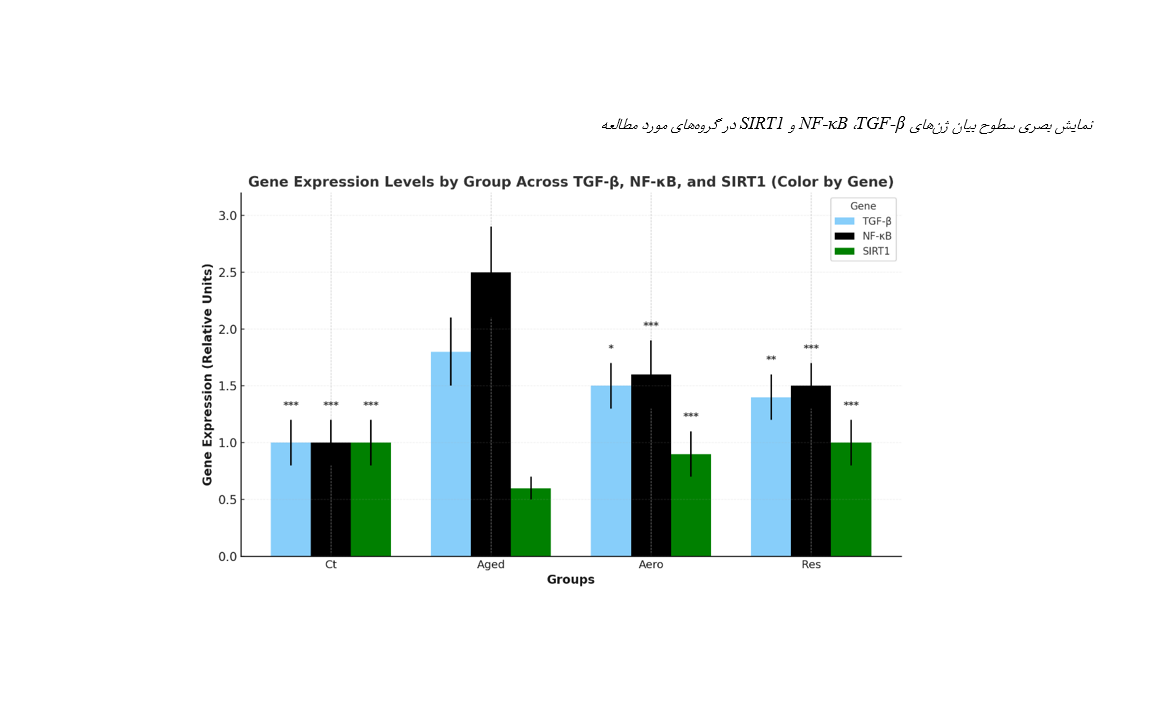
This study aimed to investigate the effects of aerobic and resistance training on irisin levels and the expression of the inflammatory genes TGF-β, NF-κB, and SIRT1 in intestinal lymphocytes of aged rats, in order to evaluate noninvasive strategies to mitigate intestinal inflammation during aging. In this laboratory trial, 32 aged male Wistar rats (18 months old) were randomly assigned to four groups: healthy control (Ct), aged without training (Aged), aged with aerobic training (Aero), and aged with resistance training (Res). Training protocols were conducted for 8 weeks (5 days per week); the aerobic group trained at moderate intensity (speed 12 m/min, up to 56 minutes), while the resistance group trained with progressively increasing loads (5% to 40% of body weight, 8 climbs per session). Gene expression was measured using Real-Time PCR, and irisin levels were measured using an ELISA kit. Data were analyzed using SPSS; two-way ANOVA was used to examine the main effects of groups and training types, Tukey's test was used for pairwise comparisons, and independent t-test was used to directly compare the aerobic and resistance groups (p < 0.05). The expression of TGF-β increased in the Aged group compared to Ct (P < 0.001) but showed a significant decrease in both training groups (Aero: 17%; Res: 22%; P < 0.05). NF-κB expression also increased in the Aged group (P < 0.001) and decreased in the training groups (Aero: 36%; Res: 40%; P < 0.001). SIRT1 expression decreased in the Aged group (P < 0.001) and increased in the training groups (Aero: 50%; Res: 67%; P < 0.001). No significant differences were found between Aero and Res for any of the three genes (P > 0.05). Irisin levels increased in both training groups, but the difference between them was not significant (P > 0.05). Aerobic and resistance training can reduce intestinal inflammation and improve intestinal health in aging. Resistance training showed stronger effects, although the differences were not statistically significant. It is recommended that resistance and aerobic training be integrated into exercise programs for the elderly to achieve optimal anti-inflammatory effects.
References
Adilakshmi, P., Suganthi, V., Rao, K. S., & Mahendran, K. B. (2023). Effect of high-intensity resistance training versus endurance training on irisin and adipomyokine levels in healthy individuals: an 8-week interventional study. Cureus, 15(10). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.46483
Al-Nimer, M. S. M. (2024). Interaction between inflammatory bowel disease, physical activity, and myokines: Assessment of serum irisin levels. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 30(22), 2923-2926. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i22.2923
Aya, V., Jimenez, P., Muñoz, E., & Ramírez, J. D. (2023). Effects of exercise and physical activity on gut microbiota composition and function in older adults: a systematic review. BMC Geriatrics, 23(1), 364. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-023-04066-y
Cart, C., & Pauling, L. (2025). The Gut Microbiome Response to Exercise. Practitioner. http://www.ifm.org/articles/the-gut-microbiome-response-to-exercise
Chen, J., Jia, S., Xue, X., Guo, C., & Dong, K. (2025). Gut microbiota: a novel target for exercise-mediated regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Frontiers in microbiology, 15, 1476908. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1476908
Das, S., Mukherjee, T., Mohanty, S., Nayak, N., Mal, P., Ashique, S., & Sharma, H. (2025). Impact of NF-κB signaling and Sirtuin-1 protein for targeted inflammatory intervention. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 26(8), 1207-1220. https://doi.org/10.2174/0113892010301469240409082212
Goodarzi, F., Nikbakht, H., Abed Natanzi, H., Ebrahim, K., & Ghazalian, F. (2020). Comparison of the effects of aerobic and resistance training on oxidative indices and TGF-β in the cardiac tissue of aged mice. Razi Journal of Medical Sciences, 27(3), 93-102. https://journals.sbmu.ac.ir/en-jnm/article/download/33437/26723/
Horn, M. A. T. A. (2016). Aging and the cardiac collagen matrix: Novel mediators of fibrotic remodeling. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology, 175, 175-185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.11.005
Hu, X., Wang, Z., Wang, W., Cui, P., Kong, C., Chen, X., & Lu, S. (2024). Irisin as an agent for protecting against osteoporosis: A review of the current mechanisms and pathways. Journal of Advanced Research, 62, 175-186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2023.09.001
Iwamoto, J., & Takeda, T. I. S. (2001). Effect of exercise training and detraining on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Journal of Orthopaedic Science, 6(2), 128-132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007760100059
Khodaverdi, H., Aghaei Bahmanbegloo, N., Rezaei-Shirazi, R., & Shadmehri, S. (2023). The effect of resistance training on muscle volume through regulation of proteins involved in the autophagy cellular pathway in aged rats. Daneshvar Medicine, 31(6), 75-83. https://daneshvarmed.shahed.ac.ir/article_4384_f452c3411a48044581e5b468c78430cf.pdf
Kim, H. J., Kim, Y. J., & Seong, J. K. (2025). Mouse models for metabolic health research: Molecular mechanism of exercise effects on health improvement through adipose tissue remodelling. Journal of Physiology, 603(2), 245-256. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP285975
Lopes, H. M., Nogueira, M. A., Alves, M. C., Carvalho, R. O., Cano, A. C. S., Soares, V. C., Izidorio, F. T., Pereira, J. D. S., Salvá, M. A., & Alves, T. V. (2024). Gut microbiota and skeletal muscle axis in sports performance through nutrological activation of irisin and microRNAs: A systematic review. International Journal of Nutrology, 17(3). https://doi.org/10.54448/ijn24303
Qiu, X., Lu, P., Zeng, X., Jin, S., & Chen, X. (2023). Study on the mechanism for SIRT1 during the process of exercise improving depression. Brain Sciences, 13(5), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13050719
Raeisi, J., Rajabi, H., Ghaedi, K., Marandi, S. M., Asadi Samani, Z., & Kazemi Nasab, F. (2015). The effect of 8 weeks of resistance training on plasma irisin levels and FNDC5 and UCP1 gene expression in the muscle and adipose tissue of male rats. Sport Physiology, 7(28), 117-130. https://spj.ssrc.ac.ir/article_592.html
Sun, Y., Wang, Y., Lin, Z., Zhang, F., Zhang, Y., Ren, T., & Lin, P. (2024). Irisin delays the onset of type 1 diabetes in NOD mice by enhancing intestinal barrier. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 265, 130857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130857
Uchida, M., Fujie, S., Yano, H., & Iemitsu, M. (2023). Aerobic exercise training‐induced alteration of gut microbiota composition affects endurance capacity. The Journal of physiology, 601(12), 2329-2344. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP283995
Wang, Z., Li, L., Yang, M., Li, B., & Hu, S. (2025). From Skeletal Muscle to Myocardium: Molecular Mechanisms of Exercise-Induced Irisin Regulation of Cardiac Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3550. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083550
Yazdannesab, N., Harmati, A., Valizadeh Oranj, A., & Ebrahimi Bastami, R. (2023). A review of the effects of sports activities on the gut microbiome of older individuals Ardabil, Iran. https://civilica.com/doc/1954678/
Zhao, Z., Zhu, Y., & Wan, D. (2025). Exercise and tissue fibrosis: recent advances in therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 16, 1557797. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2025.1557797
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 مریم اسمعیلی سیرچی (نویسنده); جمشید بنایی بروجنی; حسین مجتهدی, لیلا صرامی (نویسنده)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









