Assessment of Thermal Comfort in the Elderly Affected by Temperature Range Variation, Type, and Intensity of Environmental Noise
Keywords:
comfort, elderly, sound, elderly healthAbstract
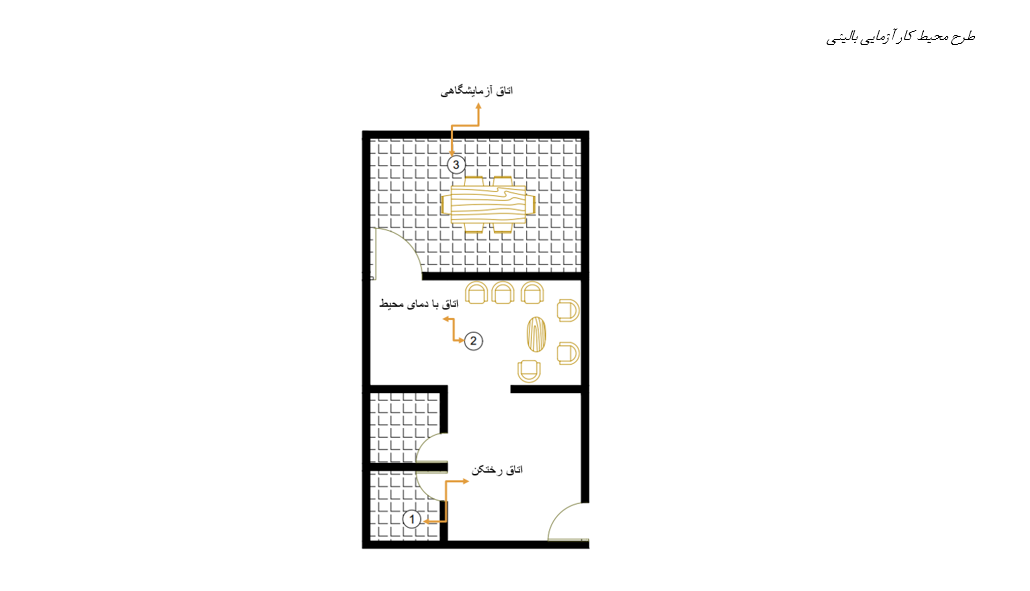
Thermal comfort significantly impacts the health and quality of life of elderly individuals. Therefore, ensuring thermal comfort is critical for the well-being of seniors, especially as they are more vulnerable to environmental changes. The purpose of this study was to examine the thermal comfort status of the elderly influenced by variations in temperature range, as well as the type and intensity of environmental noise. This experimental study included 216 elderly residents of Ilam as the statistical population. The experiment was conducted in the autumn of 2024. Participants were divided into various groups to assess the effects of temperature (20, 25, and 30 degrees Celsius), noise intensity (55, 65, 75, and 85 dB), and noise type (music, traffic, and crowd noise). Subjects were randomly assigned to groups of 72, 24, 12, and 6 participants. The collected data were analyzed using three-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) to evaluate the effects across variables. The findings indicated that different levels of temperature and noise intensity had statistically significant effects on thermal comfort perception among the elderly, with values of F(2,180)=275.665, p<0.05 and F(3,180)=0.197, p<0.05, respectively. The interaction of temperature levels with noise type also had a significant impact on the perception of thermal comfort in the elderly, with F(4,180)=17.192, p<0.05. In contrast, the factors of noise type, the interaction between temperature and noise type, temperature and noise intensity, noise type and noise intensity, and the three-way interaction of temperature, noise type, and noise intensity did not have significant effects on the elderly’s thermal comfort perception. The mean thermal comfort perception scores among the elderly for the temperature levels of 20°C, 25°C, and 30°C were -0.86, 0.13, and 1.52, respectively. The results of this study demonstrate that different levels of temperature and noise intensity significantly influence thermal comfort in the elderly. Furthermore, a significant interaction exists between temperature and noise type in affecting thermal comfort. However, factors such as noise type alone, and the interactions between temperature and noise intensity, noise type and noise intensity, and the combination of temperature, noise type, and intensity, did not have a significant impact on thermal comfort in the elderly.
References
Adib Roshan, F., Peymanizad, H., Talebpour, M., & pourezzat, A. A. (2020). Improving the Image of Future for the Elderly of 2050, Scenario Based. Journal of Iran Futures StudiesVL - 4(2), 229-261. https://doi.org/10.30479/jfs.2020.11564.1115
Baquero Larriva, M. T., & Higueras García, E. (2023). Differences in Perceptions of the Urban Acoustic Environment in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Population Ageing, 16, 781-813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12062-021-09325-7
Baquero Larriva, M. T., Mendes, A. S., & Forcada, N. J. (2022). The effect of climatic conditions on occupants' thermal comfort in naturally ventilated nursing homes. Building and Environment, 214, 108930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.108930
Bueno, A. M., de Paula Xavier, A. A., & Broday, E. E. (2021). Evaluating the connection between thermal comfort and productivity in buildings: A systematic literature review. Buildings, 11(6), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11060244
Cheraghi, M., Fattahi, K., & Omranipour, A. (2024). A survey of the impact of courtyards and vegetation in Individuals’ residences on residents' cognitive performance (case study: the residential context of the central part of Ilam city). Haft Hesar J Environ Stud, 12(47), 35-50. http://hafthesar.iauh.ac.ir/article-1-2025-fa.html
Christense, K., Doblhammer, G., Rau, R., J, W. V., Joghataei, F., Mohaqeqi Kamal, H., Basakha, M., Goharinezhad, S., Sanee, N., & Rafiey, H. (2009). Ageing populations: the challenges ahead. The LancetVL - 374, 19(4), 1196-1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61460-4 10.32598/sija.2024.3741.1
Collins, K. J., Exton-Smith, A. N., & Doré, C. J. (1981). Urban hypothermia: preferred temperature and thermal perception in old age. bmj, 282(6259), 175-177. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.282.6259.175
Ebi, K. L., Capon, A., Berry, P., Broderick, C., Richard, P., & de Dear, R. (2021). Hot weather and heat extremes: health risks. Heat and Health, 398(10301), 698-708. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01208-3
Fatahi, K., Beigi, M., Cheraghi, M., Fattahi, K., & Omranipour, A. (2024). Assessing the state of cognitive performance of employees and determining the range of thermal comfort of different genders in Ilam hospitals A survey of the impact of courtyards and vegetation in Individuals' residences on residents' cognitive performance (case study: the residential context of the central part of Ilam city). tkj, 16(3), 27-41. http://tkj.ssu.ac.ir/article-1-1324-fa.htmlhttp://hafthesar.iauh.ac.ir/article-1-2025-fa.html
Fattahi, K., Nasrollahi, N., Ansarimanesh, M., Khodakarami, J., & Omranipour, A. (2021). Investigating the role of geometry and type of urban open space on thermal comfort and environmental quality (case study of the historical fabric of Kashan). Quarterly Journal of Urban Studies, 10(39), 69-82. https://doi.org/10.34785/J011.2021.138
Fattahi, M., & Sharbatdar, M. (2023). Machine-learning-based personal thermal comfort modeling for heat recovery using environmental parameters. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 57, 103294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2023.103294
Geng, Y., HongB, Du, M., Yuan, T., & Wang, Y. (2022). Combined effects of visual-acoustic-thermal comfort in campus open spaces: A pilot study in China's cold region. Building and Environment, 209, 108658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.108658
Ghasemi, S., Keshavarz Mohammadi, N., Mohammadi Shahboulaghi, F., Ramezankhani, A., & Mehrabi, Y. (2019). Physical Health Status and Frailty Index in Community Dwelling Older Adults in Tehran. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing, 13(5), 652-665. https://doi.org/10.32598/SIJA.13.Special-Issue.652
Guan, H., Hu, S., Liu, G., & Zhang, L. (2020). The combined effects of temperature and noise on the comfort perceptions of young people with a normal Body Mass Index. Sustainable Cities and Society, 54SP - 101993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101993
Guo, Y., Gasparrini, A., B, G. A., Tawatsupa, B., Tobias, A., & Lavigne, E. (2017). Heat Wave and Mortality: A Multicountry, Multicommunity Study. Environmental Health Perspectives, 125(8), 087006. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP1026
Huang, J., Deng, F., Wu, S., LuH, Hao, y., & Guo, X. (2013). The impacts of short-term exposure to noise and traffic-related air pollution on heart rate variability in young healthy adults. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol, 23, 559-564. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2013.21
Ismaila, S. O., & Odusote, A. (2014). Noise exposure as a factor in the increase of blood pressure of workers in a sack manufacturing industry. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 3, 116-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2014.05.004
Jiao, Y., Yu, Y., Yu, H., & Wang, F. (2023). The impact of thermal environment of transition spaces in elderly-care buildings on thermal adaptation and thermal behavior of the elderly. Building and Environment, 228, 109871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109871ER -
Jin, y., Jin, h., & Kang, j. (2020). Effects of sound types and sound levels on subjective environmental evaluations in different seasons. Building and Environment, 183, 107215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.107215
Joghataei, F. A. U. M. K. H., Basakha, M., Goharinezhad, S., Sanee, N., & Rafiey, H. (2025). Well-being in Elderly: Scoping Review of Concept, Components and Indicators. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing, 19(4). https://doi.org/10.32598/sija.2024.3741.1
Mancini, D. J., & Allen, S. (2018). Geriatric physiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-72228-3_4
Mohammadian, B., Mohammadi-Shahboulaghi, F., Hosseini, M., Arsalani, N., Fallahi-Khoshknab, M., & Pirjani, P. (2024). Support Needs of Family Caregivers of Older Patients With Cancer in Iran:A Qualitative Study. Salmand: Iranian Journal of Ageing, 19(3), 484-505. https://doi.org/10.32598/sija.2023.3655.1
Nagano, K., & Horikoshi, T. (2005). New comfort index during combined conditions of moderate low ambient temperature and traffic noise. Energy and Buildings, 37(3), 287-294DO - 210.1016/j.enbuild.2004.1008.1001.
Qin, Z., Lu, B., Jing, W., Yin, Y., Zhang, L., & Wang, X. (2024). Creating comfortable outdoor environments: Understanding the intricate relationship between sound, humidity, and thermal comfort. Urban Climate, 55, 101967DO - 101910.101016/j.uclim.102024.101967.
Rashedi, V., Gharib, M., Rezaei, M., & Yazdani, A. A. (2013). Social Support and Anxiety in the Elderly of Hamedan, Iran. jrehab, 14(2), 110-115. http://rehabilitationj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-1210-en.html
Schellen, L., Van Marken Lichtenbelt, W. D., Loomans, M., Toftum, J., & De Wit, M. H. (2010). Differences between young adults and elderly in thermal comfort, productivity, and thermal physiology in response to a moderate temperature drift and a steady-state condition. Indoor Air, 20, 273-283. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0668.2010.00657.x
Soebarto, V., Zhang, H., & Schiavon, S. J. B. (2019). A thermal comfort environmental chamber study of older and younger people. Building and Environment, 155, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.03.032
Sudarsanam, N., & Kannamma, D. (2023). Investigation of summertime thermal comfort at the residences of elderly people in the warm and humid climate of India. Energy and Buildings, 291, 113151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2023.113151
Taghinezhad, Z., Eghlima, M., Arshi, M., & Pourhossein Hendabad, P. (2017). Effectiveness of Social Skills Training on Social Adjustment of Elderly People. jrehab, 18(3), 230-241. https://doi.org/10.21859/jrehab-1803230
Wang, W., Li, Y., Li, L., Wang, R., & Wang, Y. (2023). Study on thermal comfort of elderly in community parks: An exploration from the perspectives of different activities and ages. Building and Environment, 246, 111001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.111001
Wang, Z., Yu, H., Jiao, Y., Chu, X., & Luo, M. (2019). Chinese older people's subjective and physiological responses to moderate cold and warm temperature steps. Building and Environment, 149, 526-536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.12.058
Weyh, C., Krüger, K., Strasser, B., Mohammadian, B., Mohammadi-Shahboulaghi, F., Hosseini, M., Arsalani, N., Fallahi-Khoshknab, M., & Pirjani, P. (2020). Physical Activity and Diet Shape the Immune System during Aging Support Needs of Family Caregivers of Older Patients With Cancer in Iran:A Qualitative Study. Nutrients, 12(3), 622-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030622 10.32598/sija.2023.3655.1
Wu, Y., Zhang, Z., Liu, H., Li, B., Chen, B., & Kosonen, R. (2023). Age differences in thermal comfort and physiological responses in thermal environments with temperature ramp. Building and Environment, 228, 109887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109887
Yang, J., Zhou, M., Ren, Z., Li, M., Wang, B., & Liu, D. L. (2021). Projecting heat-related excess mortality under climate change scenarios in China. Nat Commun, 12, 1039. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21305-1
Yao, F., Fang, H., Han, J., Zhang, Y., Zanjari, N., Kalantari Banadaki, S. Z., Sadeghi, R., & Delbari, A. (2022). Study on the outdoor thermal comfort evaluation of the elderly in the Tibetan plateau Futures Study of the Challenges and Drivers of Population Aging in Iran Using the Scenario Analysis Technique. Sustainable Cities and Society, 77(2), 103582-103275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2021.103582 10.32598/sija.2023.3692.1
Zanjari, N., Kalantari Banadaki, S. Z., Sadeghi, R., & Delbari, A. (2024). A Futures Study of the Challenges and Drivers of Population Aging in Iran Using the Scenario Analysis TechniqueJO - A Futures Study of the Challenges and Drivers of Population Aging in Iran Using the Scenario Analysis Technique. 19(2), 258-275. https://doi.org/10.32598/sija.2023.3692.1
Zheng, G., Wei, C., You, X., & Li, K. (2023). Application of hierarchical cluster analysis in age segmentation for thermal comfort differentiation of elderly people in summer. Building and Environment, 230, 109981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.109981
Zheng, W., Shao, T., Lin, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, C., & Liu, J. (2022). A field study on seasonal adaptive thermal comfort of the elderly in nursing homes in Xi'an, China. Building and Environment, 208, 108623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.108623
Zhou, S., Li, B., Du, C., Liu, H., Wu, Y., & Hodder, S. (2023). Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 183, 113504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.113504
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Karen Fatahi; Maryam Beigi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









