Determining the Effectiveness of Zen Technique on Brain Waves in Elderly Residents of the Kahrizak Nursing Home
Keywords:
Zen technique, Alpha wave power, ElderlyAbstract
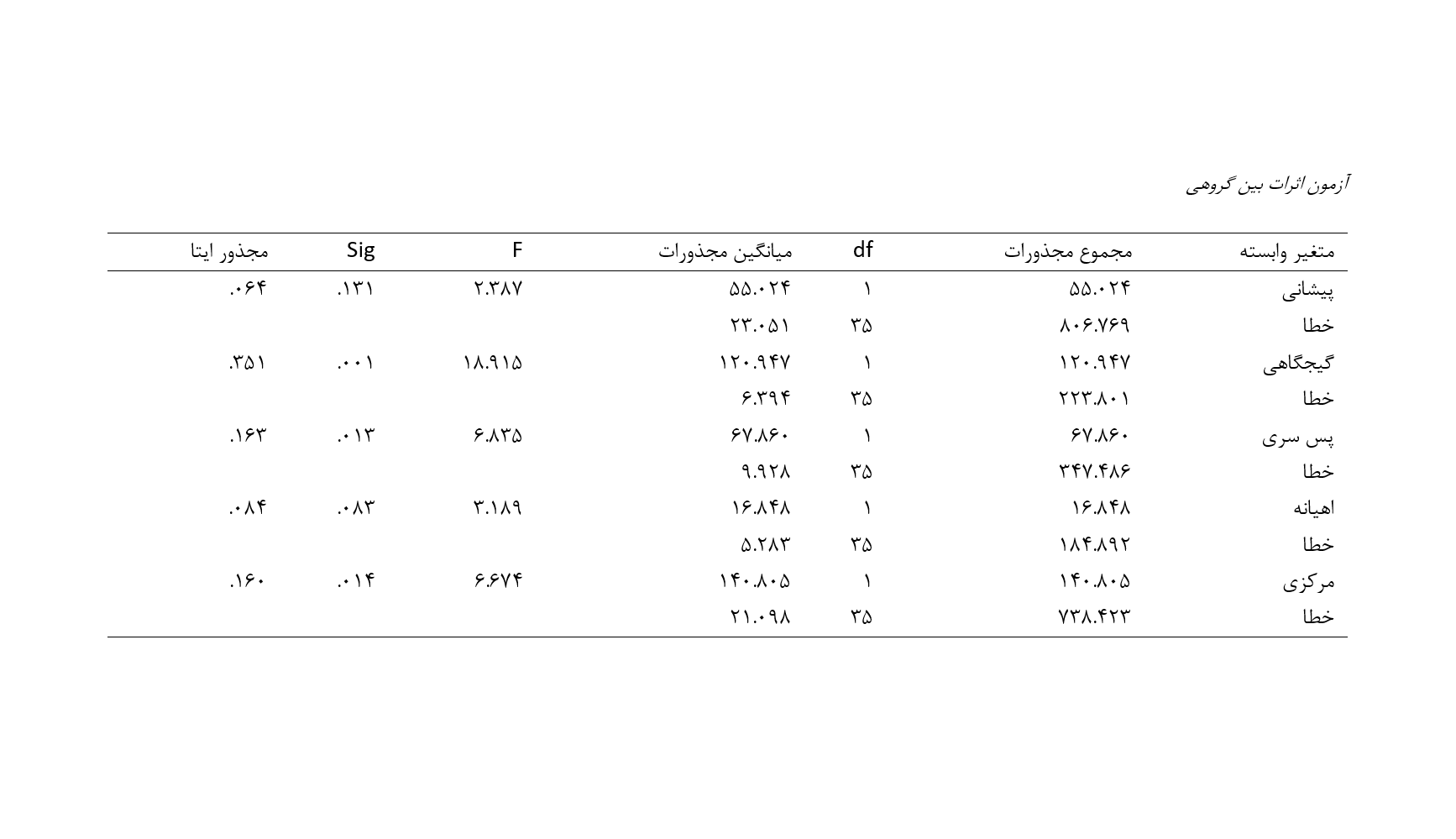
The purpose of the present study was to determine the effectiveness of the Zen technique on alpha waves in elderly residents of the Kahrizak Nursing Home. This was a quasi-experimental study with a pretest-posttest design and both experimental and control groups. The research population consisted of all elderly residents of the Kahrizak Nursing Home in Tehran in 2023. From this population, 42 individuals (20 men and 22 women) were selected through convenience sampling, and after matching based on age, gender, and cognitive status, they were randomly assigned to the experimental and control groups (21 in each group). The tools used in this study were the MoCA questionnaire for detecting mild cognitive impairment and an electroencephalograph (EEG) device. Initially, brain waves of both groups were recorded using a 19-electrode system with a Sienna 40-channel EEG device. Then, the experimental group received 20 sessions of Zen technique training, and EEG data were recorded again for both groups. Analysis was performed on the frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, and central electrodes using the EEGLAB toolbox in MATLAB software. The power of alpha waves was calculated using analysis of covariance in SPSS 26 software (P < 0.05). The results indicated that the alpha wave power in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). The dependent variables of temporal waves [F(1, 35) = 18.915, p < .001], occipital waves [F(1, 35) = 6.835, p < .001], and central waves [F(1, 35) = 6.674, p < .001] were significant, with eta-squared values showing that approximately 35% of the variance in temporal waves, 16% in occipital waves, and nearly 16% in central waves in the experimental group could be explained by the impact of Zen technique training. However, this training method did not affect the frontal and parietal scores in the posttest compared to the control group.