Nutrigenomics and Personalized Nutrition in the Context of Aging
Keywords:
Nutrigenomics, personalized nutrition, aging health, quality of life, health improvementAbstract
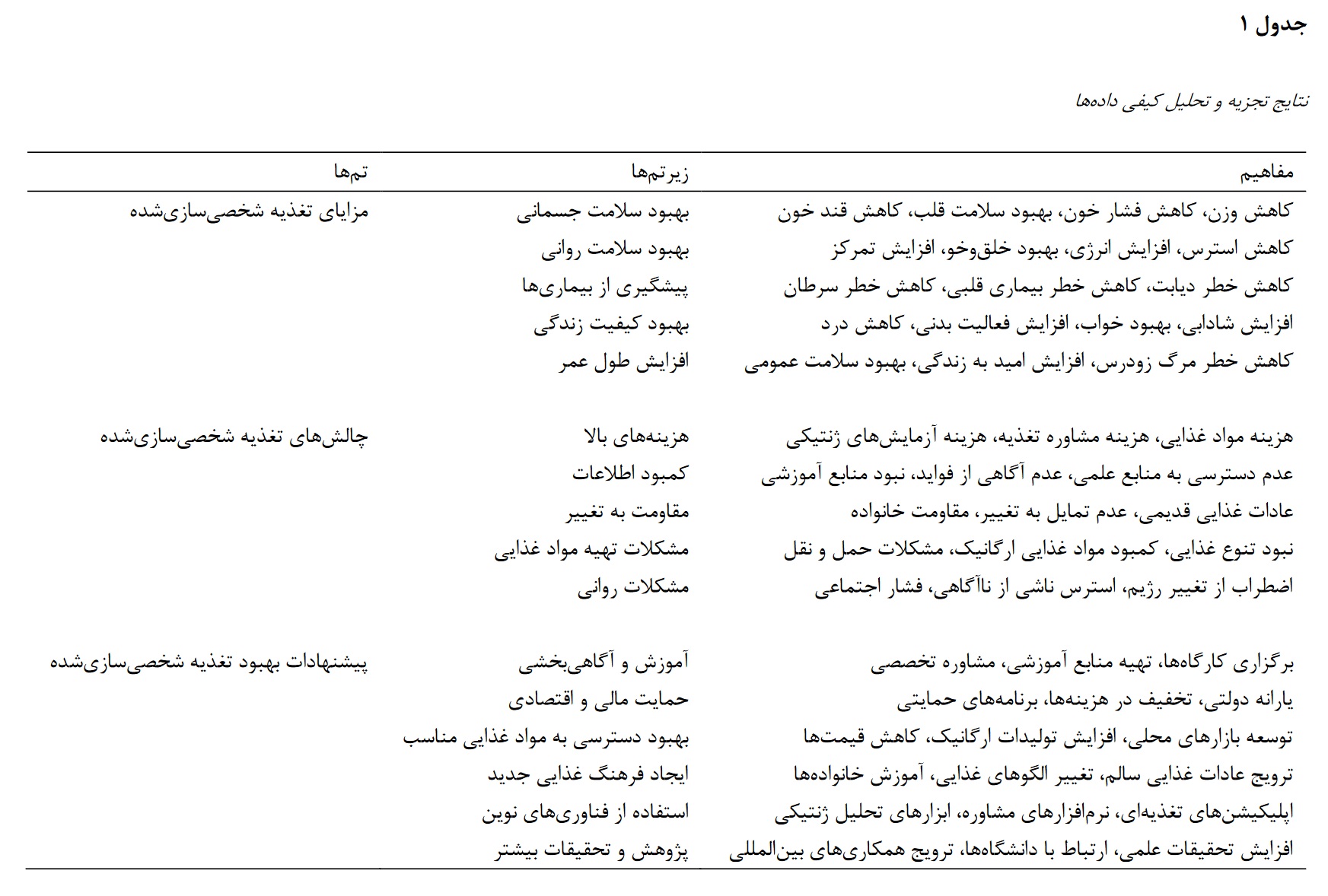
This qualitative study aimed to explore the role of nutrigenomics and personalized nutrition in improving health status and quality of life among older adults in Tehran. Using semi-structured interviews, this study engaged 24 participants aged 60 years and older from healthcare centers in Tehran. Participants were selected randomly, and interviews continued until theoretical saturation was reached. Data were analyzed using NVivo software, involving initial coding, theme development, and subtheme extraction. Analysis revealed that personalized nutrition based on nutrigenomics had positive effects on both physical and mental health of participants. Specifically, participants reported weight reduction, lower blood pressure, improved heart health, reduced blood sugar levels, decreased stress, increased energy, enhanced mood, and improved concentration. Furthermore, improvements in quality of life included increased vitality, better sleep, enhanced physical activity, and reduced pain, as well as prevention of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. The findings suggest that personalized nutrition informed by nutrigenomics can serve as an effective approach to enhance physical and mental health and improve the quality of life among older adults. However, the study’s limitations and the need for further research using quantitative methods and larger, more diverse samples to comprehensively validate these findings are acknowledged. Additionally, educational programs and economic support are essential to promote personalized nutrition and improve access to healthy food choices.