Behavioral Strategies for Enhancing Adherence to Healthy Aging Interventions
Keywords:
Healthy aging, adherence, behavioral strategies, social support, intrinsic motivation, elderlyAbstract
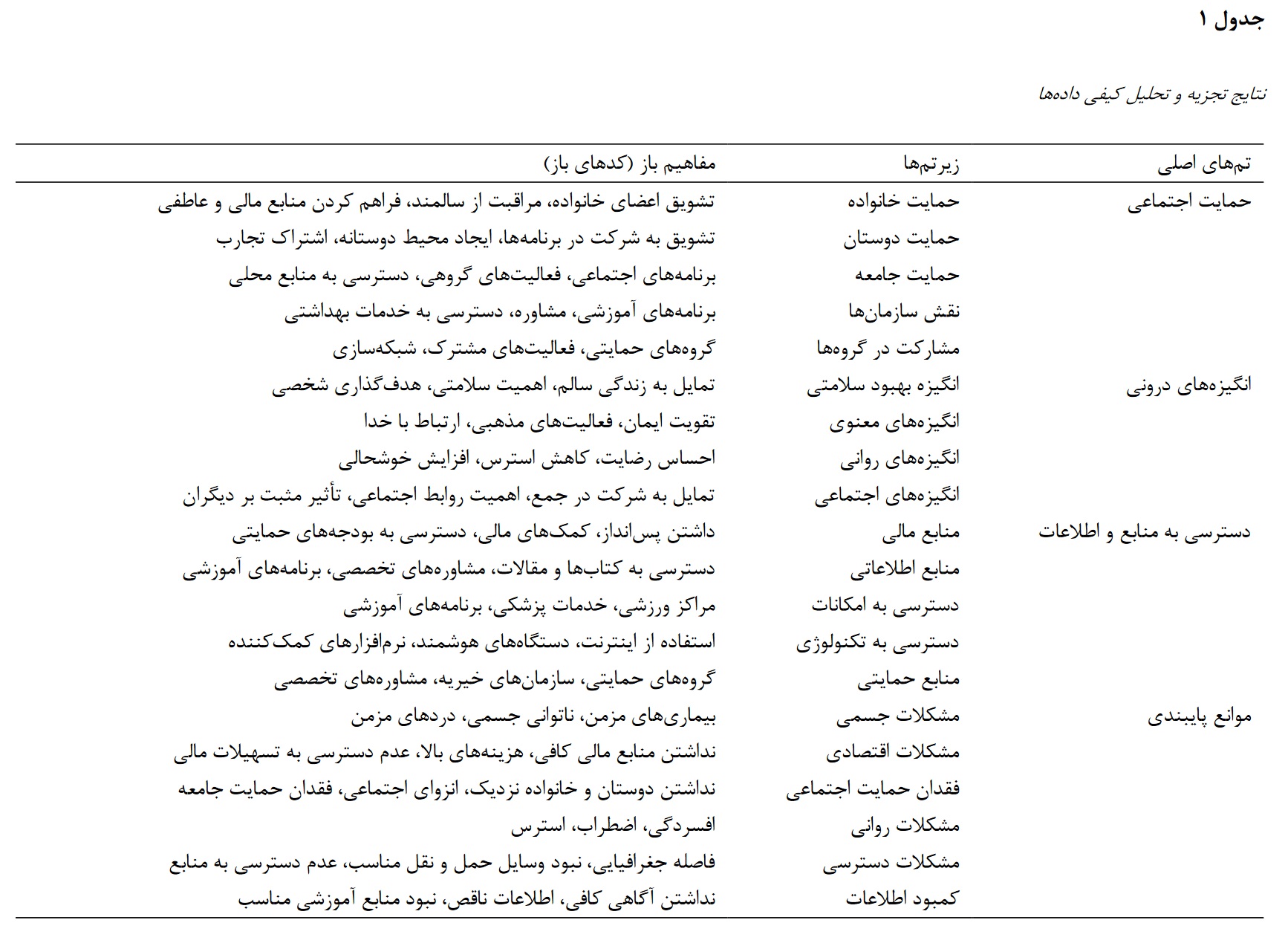
This study aims to explore behavioral strategies that enhance adherence to healthy aging interventions among elderly individuals in Tehran. It seeks to identify key factors and barriers affecting adherence to health interventions and provide practical recommendations for improving the quality of life among the elderly population. This qualitative research involved 23 elderly participants (13 women and 10 men) from Tehran, with an average age of 67 years. Data were collected through semi-structured interviews, focusing on experiences and perceptions regarding adherence to health interventions. Interviews were transcribed verbatim and analyzed using thematic analysis with NVivo software to identify key themes and sub-themes. The study continued until theoretical saturation was reached. Four main themes emerged from the analysis: social support, intrinsic motivation, access to resources and information, and barriers to adherence. Social support from family, friends, and community significantly influenced adherence to health interventions. Intrinsic motivation, including the desire for better health, stress reduction, and increased satisfaction, played a crucial role. Access to financial, informational, and technological resources was also a key factor in adherence. Barriers such as physical, economic, psychological, and social challenges were identified as significant obstacles. These findings align with previous studies emphasizing the importance of social support, motivation, and resource availability in promoting adherence to health interventions. To enhance adherence to healthy aging interventions, a multifaceted approach addressing social support, motivation, resource access, and barrier management is essential. Programs should incorporate supportive networks, educational initiatives, and accessible resources to improve the quality of life for the elderly. Future research should expand to diverse regions and incorporate mixed methods to further validate and generalize findings.