تأثیر ورزش در آب بر شاخصهای خونی منتخب، ترکیب بدنی و عملکرد حرکتی در مردان سالمند مبتلابه سارکوپنی
کلمات کلیدی:
آبی, IGF-1, فولیستاتین, چربی بدن, فعالیت حرکتی, سارکوپنیچکیده
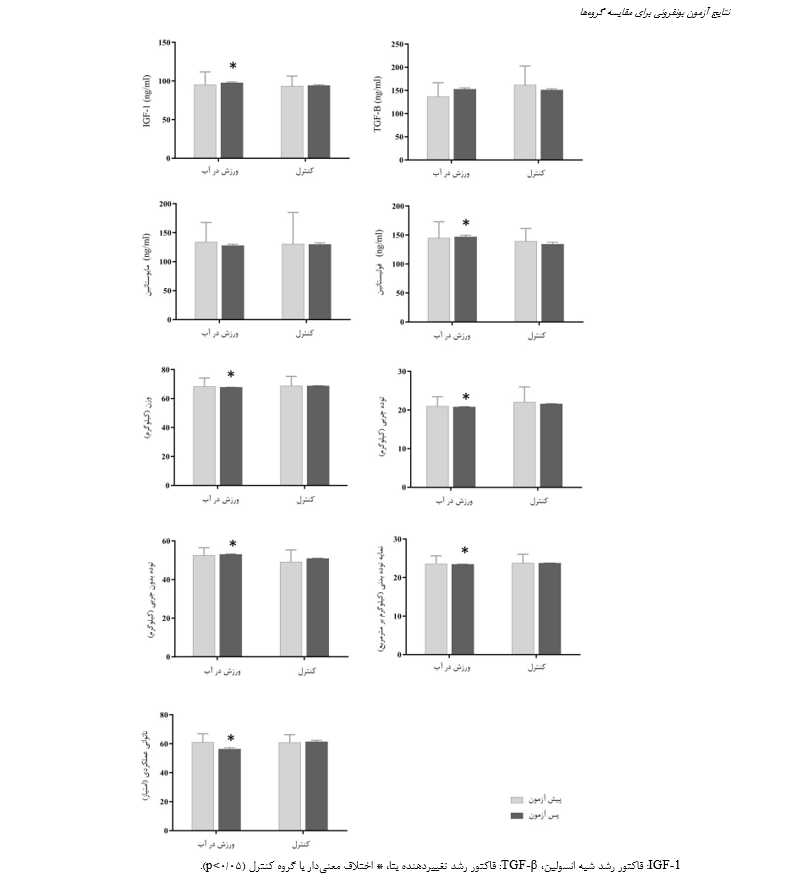
این مطالعه به بررسی اثر ورزش در آب بر تغییرات در سطوح سرمی خونی، ترکیب بدنی و عملکرد حرکتی در مردان سالمند مبتلابه سارکوپنی میپردازد. در این پژوهش، 24 سالمند سارکوپنی داوطلب که معیارهای ورود به مطالعه را داشتند، انتخاب شدند. گروه تجربی (12 نفر)، تمرینات ورزش در آب طی هشت هفته و هر جلسه تمرینی در مدت 45 دقیقه را انجام داد. سرعت حرکات برای هر دو فاز درونگرا و برونگرا 2 ثانیه، میزان افزایش بار تمرینی 1 کیلوگرم در هر شش جلسه و استراحت بین ستها 1 دقیقه پیشبینی شد. تمرینات شامل حرکات ساده در محورهای ساجیتال و فرونتال برای مفاصل هیپ، زانو و مچ پا بود و گروه کنترل (11 نفر) تنها با حضور در آب برای شش هفته پیگیری شدند. از معیارهای کارگروه اروپایی سارکوپنیا در افراد سالمند (EWGSOP) برای بررسی سارکوپنی در سالمندان و از مقیاس عملکرد حرکتی سالمندان (GLFS-25) برای سنجش عملکرد حرکتی در ابعاد مختلف زندگی روزمره سالمند استفاده شد. 5 سیسی خون از ورید بازویی آزمودنیها در حالت نشسته گرفته شد و مقادیر IGF-1 و TGF-β، مایوستاتین و فولیستاتین سرمی با استفاده از روش الایزا اندازهگیری شد. نمونههای خونی در وضعیتت نشسته، پس از 15 دقیقه استراحت در صبح از ورید بازویی گرفته شد. درنهایت از دستگاه آنالیز بدن ioi353 برای ارزیابی ترکیب بدنی استفاده شد. از آزمون تحلیل کوواریانس و آزمون تعقیبی بونفرونی در سطح معنیداری آلفای کوچکتر یا مساوی 05/0 استفاده شد. یافتههای تحقیق نشان داد که ورزش در آب منجر به بهبود سطوح سرم IGF-1 (22/0=ƞ، 027/0=p)، و فولیستاتین (36/0=ƞ، 003/0=p) مردان سالمند دارای سارکوپنی میشود. سطوح سرم TGF-β (626/0=p) و مایوستاتین (508/0=p) پس از هشت هفته که تمرینات ورزش در آب تغییرات معنیداری نشان نداد. همچنین تمرینات ورزش در آب منجر به بهبود ترکیب بدنی (وزن، توده چربی، توده عضلانی، نمایه توده بدنی) مردان سالمند شد (80/0≤ƞ، 001/0>p). درنهایت، تمرینات ورزش در آب منجر به بهبود عملکرد حرکتی مردان سالمند دارای سارکوپنی میشود (46/0=ƞ، 001/0=p). نتایج این پژوهش نشان داد که تمرینات ورزش در آب، میتواند بهعنوان یک روش ایمن و مؤثر برای بهبود برخی سطوح سرمی مرتبط با عضله از جمله IGF-1 و فولیستاتین، وضعیت ترکیب بدنی و بهبود عملکرد حرکتی در این گروه از افراد توصیه شود.
مراجع
Amiri, N., Fathei, M., & Mosaferi Ziaaldini, M. (2021). Effects of resistance training on muscle strength, insulin-like growth factor-1, and insulin-like growth factor–binding protein-3 in healthy elderly subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hormones, 20, 247-257. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-020-00250-6
Araújo, J. P., Neto, G. R., Loenneke, J. P., Bemben, M. G., Laurentino, G. C., Batista, G., Silva, J. C., Freitas, E. D., & Sousa, M. S. (2015). The effects of water-based exercise in combination with blood flow restriction on strength and functional capacity in post-menopausal women. Age, 37(6), 1-9. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-015-9851-4
Association, A. E. (2017). Aquatic fitness professional manual. Human Kinetics.
Bagheri, R., Moghadam, B. H., Church, D. D., Tinsley, G. M., Eskandari, M., Moghadam, B. H., Motevalli, M. S., Baker, J. S., Robergs, R. A., & Wong, A. (2020). The effects of concurrent training order on body composition and serum concentrations of follistatin, myostatin and GDF11 in sarcopenic elderly men. Experimental gerontology, 133, 110869. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.110869
Barbagallo, M., Veronese, N., Di Prazza, A., Pollicino, F., Carruba, L., La Carrubba, A., & Dominguez, L. J. (2022). Effect of calcifediol on physical performance and muscle strength parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients, 14(9), 1860. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091860
Barzegari Marvast, H., Akbarnejad, A., & Norouzi, J. (2024). Effect of 12 Weeks Incremental Resistance Training on Serum Levels of Myostatin, Follistatin, and IGF-I in Sedentary Elderly Men. Iranian Journal of War and Public Health, 16(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.58209/ijwph.16.1.1
Bektan Kanat, B., Suzan, V., Ulugerger Avci, G., Unal, D., Emiroglu Gedik, T., Suna Erdincler, D., Doventas, A., & Yavuzer, H. (2024). Systemic inflammatory response index and monocyte-to-high density lipoprotein ratio-new biomarkers remarking the inflammation in primary sarcopenia: The SIMPS study. Bratislava Medical Journal/Bratislavské Lekárske Listy, 125(5). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.4149/bll_2024_49
Bergamin, M., Ermolao, A., Tolomio, S., Berton, L., Sergi, G., & Zaccaria, M. (2013). Water-versus land-based exercise in elderly subjects: effects on physical performance and body composition. Clinical interventions in aging, 1109-1117. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S44198
Borst, S. E., Vincent, K. R., Lowenthal, D. T., & Braith, R. W. (2002). Effects of resistance training on insulin‐like growth factor and its binding proteins in men and women aged 60 to 85. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 50(5), 884-888. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50215.x
Çetin, B., & Menteş, A. N. (2024). Effect of Aquatic Exercises on Strength and Quality of Life in Sarcopenia Older Individuals. Turkish Journal of Sport and Exercise, 26(1), 12-19. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.15314/tsed.1395197
da Silva Gonçalves, L., da Silva, L. S. L., Benjamim, C. R., Tasinafo Jr, M., Bohn, L., Abud, G. F., Ortiz, G., & de Freitas, E. (2023). The effects of different exercise training types on body composition and physical performance in older adults with sarcopenic obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of nutrition, health and aging, 27(11), 1076-1090. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-023-2018-6
Far, M. S., Hejazi, S. M., & Boghrabadi, V. (2014). Relationship between 8 weeks exercise in water and insulin resistance. Advances in Environmental Biology, 66-71.
Francesca, A., Laura, B., Gabriella, D., Bacurau, A. V. N., Carmine, N., Emanuele, R., Nadia, R., Scicchitano, B. M., & Antonio, M. (2019). Effects of IGF‐1 isoforms on muscle growth and sarcopenia. Aging Cell, 2019(april), 1-11. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12954
Hashemi, R., Shafiee, G., Motlagh, A. D., Pasalar, P., Esmailzadeh, A., Siassi, F., Larijani, B., & Heshmat, R. (2016). Sarcopenia and its associated factors in Iranian older individuals: Results of SARIR study. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 66, 18-22. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2016.04.016
Hassan, B. H., Hewitt, J., Keogh, J. W., Bermeo, S., Duque, G., & Henwood, T. R. (2016). Impact of resistance training on sarcopenia in nursing care facilities: A pilot study. Geriatric nursing, 37(2), 116-121. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2015.11.001
Huang, L.-Y., Lim, A. Y., Hsu, C.-C., Tsai, Y.-F., Fu, T.-C., Shyu, Y.-C., Peng, S.-C., & Wang, J.-S. (2024). Sustainability of exercise-induced benefits on circulating MicroRNAs and physical fitness in community-dwelling older adults: a randomized controlled trial with follow up. BMC Geriatrics, 24(1), 473. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-024-05084-0
Irandoust, K., Taheri, M., Mirmoezzi, M., H’mida, C., Chtourou, H., Trabelsi, K., Ammar, A., Nikolaidis, P. T., Rosemann, T., & Knechtle, B. (2019). The effect of aquatic exercise on postural mobility of healthy older adults with endomorphic somatotype. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(22), 4387. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224387
Jiang, Q., Lou, K., Hou, L., Lu, Y., Sun, L., Tan, S. C., Low, T. Y., Kord-Varkaneh, H., & Pang, S. (2020). The effect of resistance training on serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 50, 102360. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102360
Kang, D.-w., Bressel, E., & Kim, D.-y. (2020). Effects of aquatic exercise on insulin-like growth factor-1, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and cognitive function in elderly women. Experimental gerontology, 132, 110842. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.110842
Lan, X.-Q., Deng, C.-J., Wang, Q.-Q., Zhao, L.-M., Jiao, B.-W., & Xiang, Y. (2024). The Role of TGF-β Signaling in Muscle Atrophy, Sarcopenia and Cancer Cachexia. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 114513. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2024.114513
Lee, I. H., Seo, E. J., & Lim, I. S. (2014). Effects of aquatic exercise and CES treatment on the changes of cognitive function, BDNF, IGF-1, and VEGF of persons with intellectual disabilities. Journal of exercise nutrition & biochemistry, 18(1), 19. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5717/jenb.2014.18.1.19
Lee, S. Y., Beom, J., Choi, J. H., Jang, H. C., Kim, E., Kim, K., Kim, M., Shim, G. Y., Won, C. W., & Lim, J.-Y. (2023). Effectiveness and clinical application of multidisciplinary combined exercise and nutrition intervention for sarcopenic older adults with metabolic syndrome: study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial. BMJ open, 13(7), e070252. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070252
Martins, W. R., Safons, M. P., Bottaro, M., Blasczyk, J. C., Diniz, L. R., Fonseca, R. M. C., Bonini-Rocha, A. C., & de Oliveira, R. J. (2015). Effects of short term elastic resistance training on muscle mass and strength in untrained older adults: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Geriatrics, 15(1), 99. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-015-0101-5
Melo, R. S., Cardeira, C. S. F., Rezende, D. S. A., Guimarães-do-Carmo, V. J., Lemos, A., & de Moura-Filho, A. G. (2023). Effectiveness of the aquatic physical therapy exercises to improve balance, gait, quality of life and reduce fall-related outcomes in healthy community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS one, 18(9), e0291193. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0291193
Oliveira, J. S., Pinheiro, M. B., Fairhall, N., Walsh, S., Franks, T. C., Kwok, W., Bauman, A., & Sherrington, C. (2020). Evidence on physical activity and the prevention of frailty and sarcopenia among older people: a systematic review to inform the World Health Organization physical activity guidelines. Journal of Physical Activity and Health, 17(12), 1247-1258. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2020-0323
Prado, C. M., Batsis, J. A., Donini, L. M., Gonzalez, M. C., & Siervo, M. (2024). Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: a clinical overview. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 20(5), 261-277. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-023-00943-z
Qi, S., Horii, N., Kishigami, K., Miyachi, M., Iemitsu, M., & Sanada, K. (2023). Effects of water exercise on body composition and components of metabolic syndrome in older females with sarcopenic obesity. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 35(1), 24-30. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.35.24
Scartoni, F. R., Machado, A. F., Bocalini, D. S., & Yázig, F. (2024). Effect of the aquatic program on strength and indicators of sarcopenia in elderly. Retos: nuevas tendencias en educación física, deporte y recreación(56), 31-39. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.47197/retos.v56.103882
Swati, S. (2022). The Role of TGF Beta Proteins In The Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Mass Swinburne].
Taheri, M., Mirmoezzi, M., & Sabaghi, M. (2018). Effects of aquatic on balance and preventing of fall among healthy elderly men. J Saf Promot Inj Prev, 6(3), 144-151.
Tokida, R., Ikegami, S., Takahashi, J., Ido, Y., Sato, A., Sakai, N., Horiuchi, H., & Kato, H. (2020). Association between musculoskeletal function deterioration and locomotive syndrome in the general elderly population: a Japanese cohort survey randomly sampled from a basic resident registry. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 21, 1-10. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-020-03469-x
Waller, B., Ogonowska-Słodownik, A., Vitor, M., Rodionova, K., Lambeck, J., Heinonen, A., & Daly, D. (2016). The effect of aquatic exercise on physical functioning in the older adult: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Age and ageing, 45(5), 593-601. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afw102
Wang, C., & Bai, L. (2012). Sarcopenia in the elderly: basic and clinical issues. Geriatrics & gerontology international, 12(3), 388-396. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00851.x
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 طول عمر

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.









