بررسی نقش شدت و حجم فعالیت بدنی در طول عمر بر بهبود عملکرد ورزشی و آمادگی جسمانی معلمان تربیت بدنی
کلمات کلیدی:
آمادگی جسمانی, ترکیب بدن, فعالیت بدنی در طول عمر, فعالیت بدنی شدید, عملکرد ورزشی, معلمان تربیت بدنیچکیده
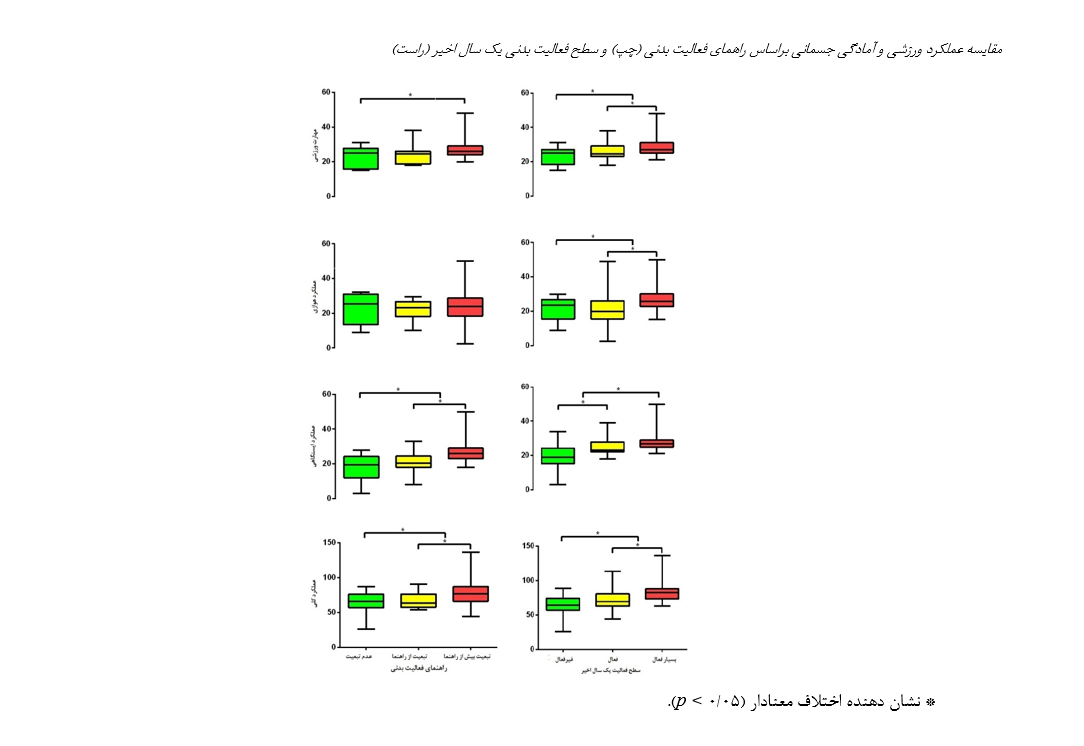
فعالیت بدنی مستمر در طول عمر نقش موثر و کلیدی بر سلامت و عملکرد جسمانی دارد؛ نقشی که برای معلمان تربیت بدنی، بهعنوان الگوهای رفتاری و کنشگران اصلی آموزش سبک زندگی فعال، اهمیت دوچندان مییابد. بااینحال، پژوهشهای محدودی به بررسی تأثیر شدت و میزان فعالیت بدنی بر عملکرد ورزشی و آمادگی جسمانی این گروه شغلی پرداختهاند. هدف مطالعه حاضر، بررسی نقش شدت و میزان فعالیت بدنی در طول عمر و فعالیت بدنی کنونی بر عملکرد ورزشی و آمادگی جسمانی معلمان تربیت بدنی مرد استان خوزستان بود. مطالعه حاضر بهصورت مقطعی انجام شد. 105 معلم مرد (میانگین سنی: 7/38±12/76سال) به روش نمونهگیری خوشهای چندمرحلهای انتخاب شدند. فعالیت بدنی در طول عمر و فعالیت بدنی کنونی بترتیب با استفاده از پرسشنامههای HLAQ و IPAQ، ترکیب بدن از طریق شاخص توده بدن، و عملکرد ورزشی و آمادگی جسمانی از طریق آزمونهای مهارتی، ایستگاهی و هوازی ارزیابی شد. فعالیت بدنی شدید در طول عمر با مهارت ورزشی (46/0=r)، عملکرد ایستگاهی (60/0=r) و عملکرد کلی (55/0=r) همبستگی قویتری نسبت به فعالیت متوسط یا کنونی نشان داد (05/0 >p). معلمان با وزن نرمال و سن کمتر عملکرد بهتری داشتند. فعالیت بدنی شدید، سن و شاخص توده بدنی بهترتیب 51%، 28% و 53% عملکرد کلی، مهارتی و ایستگاهی را پیشبینی کردند. فعالیت بدنی شدید و مستمر در طول عمر، همراه با ترکیب بدنی بهینه، نقش کلیدی در بهبود عملکرد ورزشی و آمادگی جسمانی معلمان تربیت بدنی دارد. برنامههای مداخلهای هدفمند برای تشویق فعالیتهای شدید و مدیریت وزن توصیه میشود.
مراجع
Ainsworth, B. E., Haskell, W. L., Whitt, M. C., Irwin, M. L., Swartz, A. M., Strath, S. J., O'Brien, W. L., Bassett, D. R., Schmitz, K. H., Emplaincourt, P. O., Jacobs, D. R., & Leon, A. S. (2000). Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 32(9 Suppl), S498-504. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005768-200009001-00009
Aslam, S., Habyarimana, J. D. D., & Bin, S. Y. (2025). Neuromuscular adaptations to resistance training in elite versus recre ational athletes. Frontiers in Physiology, 16, 1598149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2025.1598149
Barker, D., Quennerstedt, M., Korp, M., & Johansson, A. (2021). Fit for the job? How corporeal expectations shape physical education teachers' understandings of content, pedagogy, and the purposes of physical education. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 28(3), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1080/17408989.2021.1934664
Bloch, M., Cordovil, R., Rodrigues, L. P., Martins, C., Braga, M. L., Vale, S., Proença, R., Brito, J., Guilherme, J., Neto, C., Seabra, A., & Costa, J. A. (2025). The impact of a school-based physical activity program on children's movement behaviors, aerobic fitness and motor competence: A follow up study. Frontiers in Sports and Active Living, 7, 1541862. https://doi.org/10.3389/fspor.2025.1541862
Borodulin, K., & Anderssen, S. (2023). Physical activity: associations with health and summary of guidelines. Food & Nutrition Research, 67, 10.29219/fnr.v29267.29719. https://doi.org/10.29219/fnr.v67.9719
Campa, F., Toselli, S., Mazzilli, M., Gobbo, L. A., & Coratella, G. (2021). Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis. Nutrients, 13(5), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051620
Cheung, P. (2020). Teachers as role models for physical activity: Are preschool children more active when their teachers are active? European Physical Education Review, 26(1), 101-110. https://doi.org/10.1177/1356336X19835240
Cooper, R., Mishra, G. D., & Kuh, D. (2011). Physical activity across adulthood and physical performance in midlife : findings from a British birth cohort. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 41(4), 376-384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2011.06.035
Dimitriadis, N., Tsiampalis, T., Arnaoutis, G., Tambalis, K. D., Damigou, E., Chrysohoou, C., Barkas, F., Tsioufis, C., Pitsavos, C., Liberopoulos, E., Sfikakis, P. P., & Panagiotakos, D. (2024). Longitudinal trends in physical activity levels and lifetime cardiovascular disease risk: Insights from the ATTICA cohort study (2002-2022). Journal of Preventive Medicine and Hygiene, 65(2), E134-E144. https://doi.org/10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2024.65.2.3243
Donnelly, J. E., Hillman, C. H., Castelli, D., Etnier, J. L., Lee, S., Tomporowski, P., Lambourne, K., & Szabo-Reed, A. N. (2016). Physical Activity, Fitness, Cognitive Function, and Academic Achieveme nt in Children: A Systematic Review. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 48(6), 1197-1222. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000901
Engeroff, T., Vogt, L., Fleckenstein, J., Füzéki, E., Matura, S., Pilatus, U., Schwarz, S., Deichmann, R., Hellweg, R., Pantel, J., & Banzer, W. (2019). Lifespan leisure physical activity profile, brain plasticity and cogni tive function in old age. Aging & mental health, 23(7), 811-818. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2017.1421615
Fleg, J. L., Morrell, C. H., Bos, A. G., Brant, L. J., Talbot, L. A., Wright, J. G., & Lakatta, E. G. (2005). Accelerated longitudinal decline of aerobic capacity in healthy older adults. Circulation, 112(5), 674-682. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.545459
Franklin, B. A., Eijsvogels, T. M. H., Pandey, A., Quindry, J., & Toth, P. P. (2022). Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and cardiovascular health: A clinical practice statement of the ASPC Part I: Bioenergetics, contemporary physical activity recommendations, benefits, risks, extreme exercise regimens, potential maladaptations. American Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 12, 100424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpc.2022.100424
Ganse, B., & Degens, H. (2021). Current Insights in the Age-Related Decline in Sports Performance of the Older Athlete. International journal of sports medicine, 42(10), 879-888. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1480-7730
Gao, X., Cheng, M., & Zhang, R. (2024). The relationship between physical activity and the health of primary a nd secondary school teachers: the chain mediating effects of body imag e and self-efficacy. BMC public health, 24(1), 562. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-17914-2
Garber, C. E., Blissmer, B., Deschenes, M. R., Franklin, B. A., Lamonte, M. J., Lee, I. M., Nieman, D. C., Swain, D. P., & American College of Sports, M. (2011). American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quali ty of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, muscu loskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guida nce for prescribing exercise. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 43(7), 1334-1359. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e318213fefb
Hernandez-Martinez, J., Perez-Carcamo, J., Coñapi-Union, B., Canales-Canales, S., Negron-Molina, M., Avila-Valencia, S., Cid-Calfucura, I., Herrera-Valenzuela, T., Cisterna, D., Branco, B. H. M., & Valdés-Badilla, P. (2024). Relationship between Body Composition and Physical Performance by Sex in Professional Basketball Players. Applied Sciences, 14(20), 9165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14209165
Holtermann, A., Krause, N., Beek, A. J., & Straker, L. (2018). The physical activity paradox: six reasons why occupational physical a ctivity (OPA) does not confer the cardiovascular health benefits that leisure time physical activity does. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 52(3), 149-150. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2017-097965
Hung, C.-H., Su, C.-H., & Wang, D. (2025). The Role of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) in Neuromuscular A daptations: Implications for Strength and Power Development-A Review. Life (Basel, Switzerland), 15(4), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040657
Jose, K. A., Blizzard, L., Dwyer, T., McKercher, C., & Venn, A. J. (2011). Childhood and adolescent predictors of leisure time physical activity during the transition from adolescence to adulthood: a population base d cohort study. The International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activit y, 8, 54. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-8-54
Lee, P. H., Macfarlane, D. J., Lam, T. H., & Stewart, S. M. (2011). Validity of the international physical activity questionnaire short fo rm (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. The International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activit y, 8, 115. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-8-115
Li, J., Lim, J., Jo, H., & Kang, S.-J. (2024). Effects of Possible Sarcopenia on Physical Fitness, Gait, and Fear of Falling of Older Adults. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 53(12), 2714-2721.
Liu, Y., Yan, J., & Li, J. (2025). The relationship between physical education teachers’ competence suppo rt and middle school students’ participation in sports: A chain mediat ion model of perceived competence and exercise persistence. PLoS One, 20(1), e0314338. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0314338
Mahmoudi, O. (2022). The Structural Model of The Relationship between Motive Incongruence a nd Job Burnout with an Emphasis on the Mediating Role of Intrinsic Mot ivation among Teachers Who Graduated from Farhangian University. Teacher Professional Development, 7(3), 35-54.
Markelj, N., Kovač, M., Leskošek, B., & Jurak, G. (2024). Occupational health disorders among physical education teachers compar ed to classroom and subject specialist teachers. Frontiers in Public Health, 12, 1390424. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1390424
Martín-Rodríguez, A., Belinchón-deMiguel, P., Rubio-Zarapuz, A., Tornero-Aguilera, J. F., Martínez-Guardado, I., Villanueva-Tobaldo, C. V., & Clemente-Suárez, V. J. (2024). Advances in Understanding the Interplay between Dietary Practices, Body Composition, and Sports Performance in Athletes. Nutrients, 16(4), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040571
Moghaddam, F., & Kiani, M. (2012). Economic and social factors influencing cosmetic use among girls under 20 in Yazdanshahr, Najafabad. Journal of Skin and Beauty, 4(1), 1-9.
Moghaddam, M. B., Aghdam, F. B., Allahverdipour, H., Jafarabadi, M. A., Nikookheslat, & Safarpour, S. (2012). The Iranian Version of International Physical Activity Questionnaire ( IPAQ) in Iran: Content and Construct Validity, Factor Structure, Inter nal Consistency and Stability. World Appl Sci J, 18(8), 1073-1080. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2012.18.08.754
Moore, A. Z., Simonsick, E. M., Landman, B., Schrack, J., Wanigatunga, A. A., & Ferrucci, L. (2024). Correlates of life course physical activity in participants of the Baltimore longitudinal study of aging. Aging Cell, 23(4), e14078. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.14078
Moreira, S., Criado, M. B., Santos, P. C., Ferreira, M. S., Gonçalves, C., & Machado, J. (2022). Occupational Health: Physical Activity, Musculoskeletal Symptoms and Q uality of Life in Computer Workers: A Narrative Review. Healthcare, 10(12), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10122457
Negaresh, R., Gharakhanlou, R., Sahraian, M. A., Abolhasani, M., Motl, R. W., & Zimmer, P. (2021). Physical activity may contribute to brain health in multiple sclerosis: An MR volumetric and spectroscopy study. Journal of Neuroimaging, 31(4), 714-723.
Pelemiš, V., Pavlović, S., Mitrović, N., Nikolić, I., Stević, D., & Trajković, N. (2024). Physical Activity Levels During Physical Education Classes and Their Impact on Physical Fitness in 10-Year-Old School Children: A Comparative Study. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 9(4), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk9040220
Ramezani, A., & Kashef, M. (2017). the effect of physical education programs on physical fitness and spor ts skills, physical education teachers in different geographic areas m en and women in the country. Applied Research of Sport Management, 5(4), 33-40.
Ramezani, M., & Mirkazemi, S. A. (2025). Professional Development Strategies with an Emphasis on the Innovative Work Behavior of Physical Education Teachers in South Khorasan Province. Qualitative Research in Behavioral Sciences (QRBS), 3(2), 37-56. https://doi.org/10.22077/qrbs.2025.8364.1067
Schmidt, S. C. E., Tittlbach, S., Bös, K., & Woll, A. (2017). Different Types of Physical Activity and Fitness and Health in Adults: An 18-Year Longitudinal Study. BioMed Research International, 2017, 1785217. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1785217
Schwendinger, F., Infanger, D., Lichtenstein, E., Hinrichs, T., Knaier, R., Rowlands, A. V., & Schmidt-Trucksäss, A. (2025). Intensity or volume: the role of physical activity in longevity. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 32(1), 10-19. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjpc/zwae295
Tanaka, H., & Seals, D. R. (2008). Endurance exercise performance in Masters athletes: age-associated cha nges and underlying physiological mechanisms. The Journal of physiology, 586(1), 55-63. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141879
Wang, X., Soh, K. G., Samsudin, S., Deng, N., Liu, X., Zhao, Y., & Akbar, S. (2023). Effects of high-intensity functional training on physical fitness and sport-specific performance among the athletes: A systematic review wit h meta-analysis. PLoS One, 18(12), e0295531. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0295531
Wiesinger, H.-P., Stöggl, T. L., Haller, N., Blumkaitis, J., Strepp, T., Kilzer, F., Schmuttermair, A., & Hopkins, W. G. (2024). Meta-analyses of the effects of high-intensity interval training in el ite athletes-part I: mean effects on various performance measures. Frontiers in Physiology, 15, 1486526. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2024.1486526
Zoila, F., Filannino, F. M., Panaro, M. A., Sannicandro, I., Cianciulli, A., & Porro, C. (2025). Enhancing active aging through exercise: a comparative study of high-i ntensity interval training and continuous aerobic training benefits. Frontiers in Aging, 6, 1493827. https://doi.org/10.3389/fragi.2025.1493827
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 Raoof Negaresh, Khalil Allah Moonikh (Author)

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.









